javascript tutorial
http://www.w3schools.com/html/html_intro.asp 사이트 부터 시작
JavaScript Introduction
자바스크립트 소개
JavaScript is the most popular programming language in the world.
This page contains some examples of what JavaScript can do.
자바스크립트는 세계에서 최고로 인기있는 프로그래밍 언어입니다.
이 페이지에는 자바스크립트가 어떤동작을 하는지에대한 약간의 예제가 들어가 있습니다.
JavaScript Can Change HTML Content
자바스크립트는 HTML내용을 변경할 수 있습니다.
One of many HTML methods is getElementById().
This example uses the method to “find” an HTML element (with id=”demo”), and changes the element content (innerHTML) to “Hello JavaScript”:
getElementById()는 많은 HTML 방법중에 하나입니다.
이 예시는 HTML요소에서(with id=”demo”)를 찾아서, (innerHTML)요소안을 “Hello JavaScript”로 변경하는 방법입니다.
Example
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Hello JavaScript";
JavaScript Can Change HTML Attributes
HTML 속성은 자바스크립트에 의해서 변경하는 것이 가능합니다
This example changes an HTML image, by changing the src attribute of an tag:
이 예시는 HTML 이미지를 이미지 태그의 src속성에 의해서 바뀝니다. 링크

JavaScript Can Change HTML Styles (CSS)
자바스크립트는 HTML (CSS)스타일을 바꿀 수 있습니다.
Changing the style of an HTML element, is a variant of changing an HTML attribute:
HTML요소에서 HTML의 스타일을 변경한 결과입니다.
Example
document.getElementById("demo").style.fontSize = "25px";
JavaScript Can Validate Data
자바스크립트는 데이터 인증이 가능합니다.
JavaScript is often used to validate input:
Please input a number between 1 and 10
자바스크립트는 보통 입력의 유효성을 검사하는데 사용합니다.
1부터10사이에 숫자를 넣어보세요.
링크
Did You Know?
당신은 알고 있나요?
JavaScript and Java are completely different languages, both in concept and design.
JavaScript was invented by Brendan Eich in 1995, and became an ECMA standard in 1997.
ECMA-262 is the official name. ECMAScript 6 (released in June 2015) is the latest official version of JavaScript.
자바스크립트와 자바는 둘다 언어뿐만아니라 개념이나 만드는 방법도 다릅니다.
자바스크립트는 1995년에 Brendan Eich라는 인물에의해 발명되었고, 1997년 ECMA표준이되었다.
ECMA-262는 공식적으로 알려진 이름이다. ECMASctipt6(2015년 6월에 출시)은 자바스크립트의 공식적인 최신 버전입니다.
JavaScript Where To
자바스크립트는 어디에
JavaScript can be placed in the <body> and the <head> sections of an HTML page.
자바스크립트는 HTML페이지의 <body>나<head>부분에 배치될 수 있습니다.
The <script> Tag
In HTML, JavaScript code must be inserted between <script> and </script> tags.
스크립트 태그
HTML안에서는, 자바스크립트 코드를 <script>와</script>사이에 끼워넣어야 합니다.
<script>
Example
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "My First JavaScript";
</script>
Older examples may use a type attribute: <script type="text/javascript">.
The type attribute is not required. JavaScript is the default scripting language in HTML.
다른 예로는 이런식으로 바꾸어 사용할 수도 있습니다:<script type="text/javascript">.
그 방식은 속성이 필요하지 않습니다. 자바스크립트는 HTML의 기본 스크립트 언어입니다.
JavaScript Functions and Events
자바스크립트의 함수와 이벤트
A JavaScript function is a block of JavaScript code, that can be executed when “asked” for.
For example, a function can be executed when an event occurs, like when the user clicks a button.
You will learn much more about functions and events in later chapters.
자바스크립트의 함수에 대한 “요구”가 실행될 수 있는 자바스크립트의 코드 블록입니다. 예를들어, 어떤 함수의 이벤트의 실행이나, 어떤 사용자의 버튼이 눌리는 것과 비슷합니다. 당신은 더많은 함수와 이벤트에 대해서 이장의 뒤에서 배울것 입니다.
JavaScript in <head> or <body>
자바스크립트의 <head>와<body>안에
You can place any number of scripts in an HTML document.
Scripts can be placed in the <body>, or in the <head> section of an HTML page, or in both.
Keeping all code in one place, is always a good habit.
당신은 많은 수의 스크립트를 HTML문서에 배치할 수 있습니다. 스크립트는 <body>안이나, 또는 HTML페이지의 <head>부분이나, 또는 둘다 가능합니다. 한 곳에서 항상 모든 코드를 저장하는 것이 좋은 습관입니다.
JavaScript in <head>
자바스크립트<head>안에
In this example, a JavaScript function is placed in the <head> section of an HTML page.
The function is invoked (called) when a button is clicked:
이것을 예로들자면, 자바스크립트 함수는 HTML페이지의 <head>부분 안에 배치됩니다.
버튼이 클릭될 때 이 함수를 호출합니다:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function myFunction() {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Paragraph changed.";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My Web Page</h1>
<p id="demo">A Paragraph</p>
<button type="button" onclick="myFunction()">Try it</button>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript in <body>
자바스크립트<body>안에
In this example, a JavaScript function is placed in the <body> section of an HTML page. The function is invoked (called) when a button is clicked:
이것을 예로들자면, 자바스크립트 함수는 HTML페이지의 <body>부분 안에 배치됩니다.
버튼이 클릭될 때 함수가 호출됩니다:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>My Web Page</h1>
<p id="demo">A Paragraph</p>
<button type="button" onclick="myFunction()">Try it</button>
<script>
function myFunction() {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Paragraph changed.";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
It is a good idea to place scripts at the bottom of the body element.
This can improve page load, because HTML display is not blocked by scripts loading.
body요소 아래에 스크립트를 배치하는 것이 좋습니다. HTML 화면로드가 스크립트에 의해 차단되지 않기 때문에, 페이지로드를 향상시킬 수있습니다.
External JavaScript
외부 자바스크립트
Scripts can also be placed in external files. External scripts are practical when the same code is used in many different web pages. JavaScript files have the file extension .js. To use an external script, put the name of the script file in the src (source) attribute of the <script> tag: 스크립트는 외부에 파일로 배치 될 수도 있습니다. 코드가 같고 다양한 웹 페이지에서는 외부 스크립트를 사용하는 것이 실용적 입니다. 자바스크립트 파일의 파일확장자명은.js입니다. <script>태그의 SRC(소스) 속성에 스크립트 파일을 넣어서 외부 스크립트를 사용합니다.
Example <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script src="myScript.js"></script> </body> </html>
You can place an external script reference in <head> or <body> as you like. The script will behave as if it was located exactly where the <script> tag is located. External scripts cannot contain <script> tags. 당신은 <head>나<body>안에 당신이 원하는 곳에 외부 스크립트를 참조 할 수 있습니다. 이 <script>태그에 위치한 것처럼 스크립트가 동작합니다. 외부스크립트는 <script>태그를 포함할 수 없습니다.
External JavaScript Advantages
외부 자바스크립트의 이로운점
Placing JavaScripts in external files has some advantages:
외부 파일은 자바스크립트에 이로운점이 약간 있습니다.
- It separates HTML and code
- It makes HTML and JavaScript easier to read and maintain
-
Cached JavaScript files can speed up page loads
- 이것은 HTML과 code를 나눌 수 있습니다.
- 이것은 HTML과 자바스크립트를 쉽게 읽고 유지보수를 할 수 있습니다.
- 캐시에 저장된 자바스크립트 파일은 페이지 로드 속도를 올릴 수 있습니다.
JavaScript Output
자바스크립트 출력
JavaScript does NOT have any built-in print or display functions.
자바스크립트는 자체에서 보여주는 것과 화면에 보여주는 함수가 존재하지 않습니다.
JavaScript Display Possibilities
자바스크립트는 보여주는것이 가능합니다.
JavaScript can “display” data in different ways:
자바스크립트는 보여주는 방식에 차이가 있습니다:
- Writing into an alert box, using window.alert().
- Writing into the HTML output using document.write().
- Writing into an HTML element, using innerHTML.
-
Writing into the browser console, using console.log().
- 경고 상자 안에다가 글을 쓸때는 window.alert().를 사용합니다.
- HTML안에서 출력할 글을 쓸때는 document.write()를 사용합니다.
- HTML요소 안에 글을 쓸때는 innerHTML을 사용합니다.
- 브라우저 콘솔안에다 글을 쓸때는 console.log()를 사용합니다.
Using window.alert()
window.alert() 사용
You can use an alert box to display data:
당신은 경고상자에 데이터가 보여지게 할 수 있습니다.
Example <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>My First Web Page</h1> <p>My first paragraph.</p> <script> window.alert(5 + 6); </script> </body> </html>
Using document.write()
document.write()사용
For testing purposes, it is convenient to use document.write():
편리하게 사용하기 위해 document.write()를 다음과 같이 사용하여 테스트 해보겠습니다.
Example <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>My First Web Page</h1> <p>My first paragraph.</p> <script> document.write(5 + 6); </script> </body> </html>
Using document.write() after an HTML document is fully loaded, will delete all existing HTML:
HTML문서가 완전히 로드 된 후에 document.write()를 사용하고, 기존에 사용하던 HTML을 삭제합니다.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>My First Web Page</h1> <p>My first paragraph.</p> <button onclick="document.write(5 + 6)">Try it</button> </body> </html>
The document.write() method should be used only for testing.
document.write() 방법은 테스트일 경우에만 사용 되어야 합니다.
Using innerHTML
innerHTML사용
To access an HTML element, JavaScript can use the document.getElementById(id) method.
The id attribute defines the HTML element. The innerHTML property defines the HTML content:
HTML요소에 들어가려면, 자바스크립트의 document.getElementById(id)방법을 사용해야 합니다.
id속성은 HTML의 요소를 정의합니다. innerHTML속성은 HTML의 내용을 정의합니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>My First Web Page</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = 5 + 6;
</script>
</body>
</html>
To “display data” in HTML, (in most cases) you will set the value of an innerHTML property.
대부분의 경우에 HTML로 데이터를 표기하기 위해서, 당신은 innerHTML 속성의 값을 설정 해야합니다.
Using console.log()
console.log()사용
In your browser, you can use the console.log() method to display data.
Activate the browser console with F12, and select “Console” in the menu.
console.log()메소드를 사용해서 당신의 브라우저 안에서 데이터를 볼 수 있습니다. F12로 브라우저의 콘솔을 활성화 시키고, 메뉴에서 콘솔을 선택합니다.
Example <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h1>My First Web Page</h1> <p>My first paragraph.</p> <p id="demo"></p> <script> console.log(5 + 6); </script> </body> </html>
JavaScript Syntax
자바스크립트 문법
JavaScript syntax is the set of rules, how JavaScript programs are constructed.
자바스크립트 문법은, 어떻게 자바스크립트 프로그램이 만들어지는가에 대한 규칙입니다.
JavaScript Programs
자바스크립트 프로그램
A computer program is a list of “instructions” to be “executed” by the computer.
In a programming language, these program instructions are called statements.
JavaScript is a programming language.
JavaScript statements are separated by semicolons.
컴퓨터에서의 목록중에 ‘지시’로 ‘실행’되는것이 컴퓨터 프로그램입니다.
프로그램 언어 안에서는 프로그램 명령들을 statements라고 불립니다.
자바스크립트는 프로그래밍 언어입니다.
자바스크립트 statements는 세미콜론으로 구분됩니다.
Example var x = 5; var y = 6; var z = x + y;
In HTML, JavaScript programs can be executed by the web browser.
HTML안에서의, 자바스크립트 프로그램은 웹 브라우저에서 실행이 가능 합니다.
JavaScript Statements
자바스크립트 Statements
JavaScript statements are composed of:
Values, Operators, Expressions, Keywords, and Comments.
자바스크립트 statements의 구성:
Values, Operators, Expressions, Keywords, and Comments.
JavaScript Values
자바스크립트 값
The JavaScript syntax defines two types of values: Fixed values and variable values.
Fixed values are called literals. Variable values are called variables.
자바스크립트 문법의 값의 두가지 유형으로는 : 고정된 값과 변경되는 값 입니다.
고정된 값은 리터럴(상수) 이라고 불린다. 변하는 값은 변수라고 한다.
JavaScript Literals
자바스크립트 상수
The most important rules for writing fixed values are:
Numbers are written with or without decimals:
고정된 값을 쓸때 가장 중요한 점:
숫자를 소수점이 없이 쓰일경우:
10.50 1001
Strings are text, written within double or single quotes:
문자열에 글씨는, 따옴표 또는 쌍따옴표 안에서 쓰입니다:
"John Doe" 'John Doe'
JavaScript Variables
자바스크립트 변수
In a programming language, variables are used to store data values.
JavaScript uses the var keyword to define variables.
An equal sign is used to assign values to variables.
In this example, x is defined as a variable. Then, x is assigned (given) the value 6:
프로그래밍 언어에서 변수는 데이터 값을 저장하는데 사용합니다.
자바스크립트에서는 변수의 핵심단어를 var로 정의하여 사용합니다.
=은 변수에 값을 할당하는데 사용합니다.
예제에서는 x는 변수로 정의 합니다. 그 다음에 x에 6이라는 값으로 부여합니다.
var x; x = 6;
JavaScript Operators
자바스크립트 연산자
JavaScript uses an assignment operator ( = ) to assign values to variables:
자바스크립트 대입 연산자(=)를 사용해서 변수에 값을 부여합니다:
var x = 5; var y = 6;
JavaScript uses arithmetic operators ( + - * / ) to compute values:
자바스크립트의 산수연산자로는(+ - * /)로 값을 계산합니다:
(5 + 6) * 10
JavaScript Expressions
자바스크립트 표현
An expression is a combination of values, variables, and operators, which computes to a value.
The computation is called an evaluation.
For example, 5 * 10 evaluates to 50:
expression은 값, 변수, 연산자들의 어떤 값에 대한 결과물입니다.
그 계산 값은 evaluation라고 불립니다.
예를들어 5*10의 결과는 50입니다:
5 * 10
Expressions can also contain variable values:
게다가 Expressions는 변수에 들어있는 값으로도 가능합니다:
x * 10
The values can be of various types, such as numbers and strings.
For example, “John” + “ “ + “Doe”, evaluates to “John Doe”:
이미 앞에 언급한 문자나 숫자도 다양한 종류의 값으로 가능합니다.
예를들어, “John” + “ “ + “Doe”은 “John Doe”로 평가 됩니다:
"John" + " " + "Doe"
JavaScript Keywords
자바스크립트 키워드
JavaScript keywords are used to identify actions to be performed.
The var keyword tells the browser to create a new variable:
자바스크립트 키워드는 실행될 동작을 식별할 때 사용 됩니다.
var키워드는 브라우저에서 새로운 변수를 만드는 것을 말합니다.
var x = 5 + 6; var y = x * 10;
JavaScript Comments
자바스크립트 주석
Not all JavaScript statements are “executed”.
Code after double slashes // or between /* and */ is treated as a comment.
Comments are ignored, and will not be executed:
모든 자바스크립트의 statements가 전부 “실행”되는 것은 아닙니다.
주석은 2개의 슬레쉬// 다음에 아니면 /* 와 */ 사이에 코드의 내용을 처리합니다.
주석은 무시되고, 실행되지 않습니다.
var x = 5; // I will be executed // var x = 6; I will NOT be executed
JavaScript Identifiers
자바스크립트 식별자
Identifiers are names.
In JavaScript, identifiers are used to name variables (and keywords, and functions, and labels).
The rules for legal names are much the same in most programming languages.
In JavaScript, the first character must be a letter, an underscore (_), or a dollar sign ($).
Subsequent characters may be letters, digits, underscores, or dollar signs.
Numbers are not allowed as the first character.
This way JavaScript can easily distinguish identifiers from numbers.
식별자의 이름들입니다.
자바스크립트에서는, 변수에 식별자의 이름을 사용합니다(키워드, 함수, 라벨).
합법적인 이름에대한 규칙은 대부분의 프로그밍 언어들에서 같습니다.
식별자를 구성하는 첫번째 글자는 반드시’문자’나’밑줄_‘이나 ‘달러$’로 시작되어야 합니다.
첫글자 다음 문자로는 ‘문자’ ‘숫자’ ‘밑줄_’ 또는 ‘달러$’ 표시를 할 수 있습니다.
숫자는 문자의 첫번째로 오는것은 허용하지 않습니다.
자바스크립트는 숫자로 식별자를 쉽게 구별할 수 있습니다.
JavaScript is Case Sensitive
자바스크립트 대소문자를 구별합니다.
All JavaScript identifiers are case sensitive.
The variables lastName and lastname, are two different variables.
모든 자바스크립트 식별자는 대소문자를 구별합니다.
변수lastName과 lastname 2개는 다른 변수 입니다.
lastName = "Doe"; lastname = "Peterson";
JavaScript does not interpret VAR or Var as the keyword var.
자바스크립트는 VAR또는Var로 해석하지 않고 키워드는 var 입니다.
JavaScript and Camel Case
자바스크립트 와 낙타대문자
Historically, programmers have used three ways of joining multiple words into one variable name:
Hyphens:
first-name, last-name, master-card, inter-city.
Underscore:
first_name, last_name, master_card, inter_city.
Camel Case:
FirstName, LastName, MasterCard, InterCity.
역사적으로, 프로그래머들은 하나의 변수이름에 여러가지 단어를 결합하는 방법으로 세 가지 방법이 있습니다:
하이픈: - first-name, last-name, master-card, inter-city.
밑줄: _ first_name, last_name, master_card, inter_city.
낙타대문자: FirstName, LastName, MasterCard, InterCity.
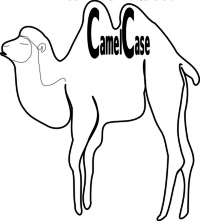
In programming languages, especially in JavaScript, camel case often starts with a lowercase letter:
firstName, lastName, masterCard, interCity.
Hyphens are not allowed in JavaScript. It is reserved for subtractions.
자바스크립트 프로그래밍 언어에서는 종종 낙타대문자의 시작이 소문자로 시작하는 경우도 종종있다.
firstName, lastName, masterCard, interCity.
하이픈은 자바스크립트에서 사용할수 없습니다. 그것은 빼기로 예약하였습니다.
JavaScript Character Set
자바스크립트 문자 세트
JavaScript uses the Unicode character set.
Unicode covers (almost) all the characters, punctuations, and symbols in the world.
For a closer look, please study our Complete Unicode Reference.
자바스크립트는 유니코드 문자 세트를 사용합니다.
유니코드는 (거의)세상의 모든 문자,문장 부호 및 기호를 포함 합니다.
끝내기전에 잠깐 들여다 보실려면, 유니코드에 대해서 부가적으로 공부하시려면 여기에 있습니다.
JavaScript Statements
자바스크립트 Statements
In HTML, JavaScript statements are “instructions” to be “executed” by the web browser.
HTML안에서 자바스크립트 statements는 웹브라우저의 지시와 지침 입니다.
JavaScript Statements
자바스크립트 Statements
This statement tells the browser to write “Hello Dolly.” inside an HTML element with id=”demo”:
이 문장은 브라우저에 HTML 내부 요소 id=”demo”에 “Hello Dolly”를 쓰는 것을 말합니다.
Example
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Hello Dolly.";
JavaScript Programs
자바스크립트 프로그램
Most JavaScript programs contain many JavaScript statements.
The statements are executed, one by one, in the same order as they are written.
In this example, x, y, and z is given values, and finally z is displayed:
최고의 자바스크립트 프로그램에는 많은 자바스크립트 statements들이 들어 있습니다.
그 문은 입력한 순서와 동일한 순서로 하나하나씩 순차적으로 실행 됩니다.
이 예제는 x, y에 값을 주고 마지막으로 z에 표시합니다.
Example
var x = 5;
var y = 6;
var z = x + y;
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = z;
JavaScript programs (and JavaScript statements) are often called JavaScript code.
자바스크립트 프로그램은 흔히 자바스크립트 코드라고도 불립니다.
Semicolons ;
세미콜론;
Semicolons separate JavaScript statements.
Add a semicolon at the end of each executable statement:
세미콜론은 자바스크립트 statements를 분리합니다.
각각의 실행 문장 끝에 세미콜론을 추가합니다.
a = 5; b = 6; c = a + b;
When separated by semicolons, multiple statements on one line are allowed:
세미콜론으로 많은 문장을 한줄에 구역을 나누어 사용할 수 있습니다.
a = 5; b = 6; c = a + b;
On the web, you might see examples without semicolons.
Ending statements with semicolon is not required, but highly recommended.
웹에는 당신의 세미콜론이 없는 예제가 보일 것 입니다.
끝에 세미콜론을 붙이는 것이 필수는 아니지만, 세미콜론을 붙이는 것을 추천 합니다.
JavaScript White Space
자바스크립트 공백
JavaScript ignores multiple spaces. You can add white space to your script to make it more readable.
The following lines are equivalent:
자바스크립트는 여러 공백을 무시합니다. 당신이 잘 읽을 수 있도록 공백을 추가할 수 있습니다.
다음에 나오는 줄들은 동일 합니다.
var person = "Hege"; var person="Hege";
A good practice is to put spaces around operators ( = + - * / ):
좋은 방법은 연산자의 주위에 공백을 넣는 것 입니다.
var x = y + z;
JavaScript Line Length and Line Breaks
자바스크립트 줄 길이와 줄바꿈
For best readability, programmers often like to avoid code lines longer than 80 characters.
If a JavaScript statement does not fit on one line, the best place to break it, is after an operator:
최고의 가독성을 위해서, 프로그램 라인의 길이가 80자 보다 길은 코드는 피하는 것이 좋습니다.
만약 자바스크립트 문이 한줄에 끝나지 않는경우에, 더좋은 방법은 연산자에서 줄바꿈 하는 것입니다.
Example
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML =
"Hello Dolly.";
JavaScript Code Blocks
자바스크립트 코드묶음
JavaScript statements can be grouped together in code blocks, inside curly brackets {…}.
The purpose of code blocks is to define statements to be executed together.
One place you will find statements grouped together in blocks, are in JavaScript functions:
자바스크립트 statements는 {…}내부 코드로 묶어 그룹화 할 수 있습니다.
코드 묶음의 목적은 문장이 같이 실행되는 것을 정의합니다.
자바스크립트 함수 안에서 당신은 그룹화된 문장을 찾을 수 있습니다.
Example
function myFunction() {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Hello Dolly.";
document.getElementById("myDIV").innerHTML = "How are you?";
}
In this tutorial we use 4 spaces of indentation for code blocks.
You will learn more about functions later in this tutorial.
우리는 이 튜토리얼의 코드 블록의 4곳에서 들여쓰기를 사용했습니다.
우리는 더 많은 함수의 기능에 대해서 다음에 자세하게 배울 것입니다.
JavaScript Keywords
자바스크립트 핵심
JavaScript statements often start with a keyword to identify the JavaScript action to be performed.
Here is a list of some of the keywords you will learn about in this tutorial:
자바스크립트에서 자주 쓰이는 핵심적인 자바스크립트의 실행방법을 확인해 보겠습니다.
다음 튜토리얼에서 배울 일부 핵심 목록 입니다.
- break: Terminates a switch or a loop
- continue: Jumps out of a loop and starts at the top
- debugger: Stops the execution of JavaScript, and calls (if available) the debugging function
- do … while: Executes a block of statements, and repeats the block, while a condition is true
- for: Marks a block of statements to be executed, as long as a condition is true
- function: Declares a function
- if … else: Marks a block of statements to be executed, depending on a condition
- return: Exits a function
- switch: Marks a block of statements to be executed, depending on different cases
- try … catch: Implements error handling to a block of statements
-
var: Declares a variable
- break: 스위치나 루프 종료합니다.
- continue: 루프 점프나 상단에서 시작합니다.
- debugger: 자바스크립트의 실행을 중지하고 디버그 함수를 호출합니다.
- do … while: 조건이 true일 동안에 블록 문장을 반복적으로 실행합니다.
- for: 명령문 블록이 실행되는 동안에 true상태이기만 하면 실행 됩니다.
- function: 함수를 선언합니다.
- if … else: 표시된 문장의 블록 조건에 따라 실행됩니다.
- return: 함수를 종료합니다.
- switch: 표시된 문장 블록은 경우에 따라 실행됩니다.
- try … catch: 문장 블록의 오류를 처리합니다.
- var: 변수를 선언합니다.
JavaScript keywords are reserved words. Reserved words cannot be used as names for variables.
자바스크립트 키워드는 예약어 입니다. 예약어는 변수 이름으로 사용 할 수 없습니다.
JavaScript Comments
자바스크립트 주석
JavaScript comments can be used to explain JavaScript code, and to make it more readable.
JavaScript comments can also be used to prevent execution, when testing alternative code.
자바스크립트 주석은 자바스크립트 코드를 설명하는데 사용하거나 가독성을 위해 사용합니다.
자바스크립트 주석은 코드를 테스트를 하거나 보이지 않게 하기위해서 사용이 가능합니다.
Single Line Comments
각 줄의 주석
Single line comments start with //.
Any text between // and the end of the line, will be ignored by JavaScript (will not be executed).
This example uses a single line comment before each line, to explain the code:
각 줄의 주석의 시작은 //로 합니다.
// 와 줄의 끝 사이에 글은 자바스크립트에서 무시됩니다.(제거되어 보이지 않습니다.)
이 예제는 각줄을 설명하기 위해 줄의 앞에 주석을 사용한 코드 예제 입니다.
Example
// Change heading:
document.getElementById("myH").innerHTML = "My First Page";
// Change paragraph:
document.getElementById("myP").innerHTML = "My first paragraph.";
This example uses a single line comment at the end of each line, to explain the code:
이 예제는 각각의 주석이 한줄의 끝까지 인것을 설명하는 코드 입니다.
Example var x = 5; // Declare x, give it the value of 5 var y = x + 2; // Declare y, give it the value of x + 2
Multi-line Comments
여러줄의 주석
Multi-line comments start with /* and end with */. Any text between /* and */ will be ignored by JavaScript. This example uses a multi-line comment (a comment block) to explain the code: 여러줄의 주석의 시작은 /* 로 시작하여 */로 끝납니다. 이것은 /* 와 */ 사이에 문자는 자바스크립트에서 무시합니다. 이 예제는 여러줄의 주석을 사용한 코드에 대한 설명 입니다.
Example
/*
The code below will change
the heading with id = "myH"
and the paragraph with id = "myP"
in my web page:
*/
document.getElementById("myH").innerHTML = "My First Page";
document.getElementById("myP").innerHTML = "My first paragraph.";
It is most common to use single line comments.
Block comments are often used for formal documentation.
이것은 흔히 사용하는 단일 주석입니다.
블록 주석은 종종 공식 문서에 사용됩니다.
Using Comments to Prevent Execution
실행 방지를 위한 주석사용
Using comments to prevent execution of code, is suitable for code testing.
Adding // in front of a code line changes the code lines from an executable line to a comment.
This example uses // to prevent execution of one of the code lines:
적절한 코드에 대한 테스트를 위해서 주석을 사용해 코드의 실행을 방지할 수 있습니다.
변경될 코드 앞에 // 를 추가해서 주석으로 실행할 수 있습니다.
이 예제는 //로 한줄의 실행을 방지한 코드 입니다.
Example
//document.getElementById("myH").innerHTML = "My First Page";
document.getElementById("myP").innerHTML = "My first paragraph.";
This example uses a comment block to prevent execution of multiple lines:
이 예제는 주석을 블록단위로 사용하여 여러줄의 실행을 방지한 것 입니다:
Example
/*
document.getElementById("myH").innerHTML = "My First Page";
document.getElementById("myP").innerHTML = "My first paragraph.";
*/
JavaScript Variables
자바스크립트 변수
JavaScript Variables
자바스크립트 변수
JavaScript variables are containers for storing data values.
In this example, x, y, and z, are variables:
자바스크립트 변수는 컨테이너에 데이터 값을 저장하는 것입니다.
x,y,z에 대한 변수 예제 입니다.
Example var x = 5; var y = 6; var z = x + y;
From the example above, you can expect:
당신은 위에서 본 예제에서 예상할 수 있을 것입니다.
- x stores the value 5
- y stores the value 6
-
z stores the value 11
- x에 5값을 저장
- y에 6값을 저장
- z에 11값을 저장
Much Like Algebra
수학과 많이 비슷합니다.
In this example, price1, price2, and total, are variables:
예제 안에는 price1, price2, total의 변수 입니다:
Example var price1 = 5; var price2 = 6; var total = price1 + price2;
In programming, just like in algebra, we use variables (like price1) to hold values.
In programming, just like in algebra, we use variables in expressions (total = price1 + price2).
From the example above, you can calculate the total to be 11.
JavaScript variables are containers for storing data values.
우리는 프로그램안에서 그냥 변수에 수를 넣어서 수학적으로 사용합니다.
우리는 프로그램안에서 변수를 수학적으로 표현합니다.
JavaScript Identifiers
자바스크립트 식별자
All JavaScript variables must be identified with unique names.
These unique names are called identifiers.
Identifiers can be short names (like x and y), or more descriptive names (age, sum, totalVolume).
The general rules for constructing names for variables (unique identifiers) are:
모든 자바스크립트 변수는 고유의 식별자 이름을 필요로 합니다.
식별자 이름은 고유의 이름으로 불립니다.
식별자는 짧은 x나y처럼 짧은 이름이나 무언가를 설명하는 age,sum,totalVolume으로도 사용이 사능합니다.
일반적인 규칙은 변수는 고유의 식별자 이름으로 구성됩니다.
- Names can contain letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs.
- Names must begin with a letter
- Names can also begin with $ and _ (but we will not use it in this tutorial)
- Names are case sensitive (y and Y are different variables)
-
Reserved words (like JavaScript keywords) cannot be used as names
- 이름안에는 달러나, 알파벳이나, 수학기호나, 밑줄로 사용이 가능합니다.
- 이름을 시작할때는 영문으로 시작합니다.
- 이름은 달러나 _로도 시작이 가능합니다.(하지만 우리 튜토리얼에서는 사용하지 않습니다)
- 이름은 대소문자를 구분합니다.(Y와y는 다른변수 입니다)
- 예약어(자바스크립트 키워드)는 이름으로 사용할 수 없습니다.
JavaScript identifiers are case-sensitive.
스크립트는 식별자는 대소문자를 구별합니다.
The Assignment Operator
할당 연산자
In JavaScript, the equal sign (=) is an “assignment” operator, not an “equal to” operator.
This is different from algebra. The following does not make sense in algebra:
자바스크립트의 = 는 같다는 의미의 연산자가 아닌 할당 연산자 입니다.
이것은 수학적인 것과 다릅니다. 다음은 수학적인 이치에 맞지 않습니다.
x = x + 5
In JavaScript, however, it makes perfect sense: it assigns the value of x + 5 to x.
(It calculates the value of x + 5 and puts the result into x. The value of x is incremented by 5.)
자바스크립트 안에서는 정확하게 x + 5의 값을 x에 할당합니다.
(그것은 x에 x+5의 결과를 계산하여 넣습니다. x값은 5에 의해 증가됩니다.)
The “equal to” operator is written like == in JavaScript.
자바스크립트 에서는 같다는 표시를 == 로 쓰여집니다.
JavaScript Data Types
자바스크립트 데이터 형식
JavaScript variables can hold numbers like 100, and text values like “John Doe”.
In programming, text values are called text strings.
JavaScript can handle many types of data, but for now, just think of numbers and strings.
Strings are written inside double or single quotes. Numbers are written without quotes.
If you put quotes around a number, it will be treated as a text string.
자바스크립트 변수는 100과 같은 숫자나, 문자 값은 “John Doe”으로 할 수 있습니다.
프로그래밍 안에서 문자값은 문자열로 불립니다.
자바스크립트는 많은 형식의 데이터를 다룰수 있습니다, 하지만 지금은 숫자와 문자열만 생각하겠습니다.
문자열은 쌍따옴표 사이에 문자가 쓰입니다. 숫자는 따옴표 없이 쓰여집니다.
만약 당신이 따옴표에 숫자를 넣었으면 그것은 문자열로 취급될 것 입니다.
Example var pi = 3.14; var person = "John Doe"; var answer = 'Yes I am!';
Declaring (Creating) JavaScript Variables
자바스크립트 변수 선언(변수를 만들다)
Creating a variable in JavaScript is called “declaring” a variable.
You declare a JavaScript variable with the var keyword:
자바스크립트에서는 변수 선언으로 변수를 만들수 있습니다.
당신은 자바스크립트 변수를 var keyword로 선언합니다.
var carName;
After the declaration, the variable has no value. (Technically it has the value of undefined)
To assign a value to the variable, use the equal sign:
선언한 다음에, 변수는 값이 없습니다. (말하자면 값이 의미를 가지고 있지 않다) 변수에 값을 할당할때는 =를 사용합니다.
carName = "Volvo";
You can also assign a value to the variable when you declare it:
당신은 변수를 선언할때 값을 넣는 것이 가능합니다.
var carName = "Volvo";
In the example below, we create a variable called carName and assign the value “Volvo” to it.
Then we “output” the value inside an HTML paragraph with id=”demo”:
아래 예제는 우리가 carName으로 불리는 것에 값으로 “Volvo”라고 넣어서 만들 변수 입니다.
그것은 우리가 HTML 단락의 id=”demo”안에다가 값을 같이 넣어야 출력 됩니다.
Example
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
var carName = "Volvo";
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = carName;
</script>
It’s a good programming practice to declare all variables at the beginning of a script.
스크립트가 시작할때 변수를 선언하는 것이 좋은 프로그래밍 입니다.
One Statement, Many Variables
하나의 문장, 많은 변수
You can declare many variables in one statement.
Start the statement with var and separate the variables by comma:
당신은 하나의 문장에 많은 변수를 선언하는 것이 가능 합니다.
문장을 시작할때 변수에 콤마로 var의 구역을 나눌수 있습니다.
var person = "John Doe", carName = "Volvo", price = 200;
A declaration can span multiple lines:
선언은 여러줄에 할 수 있습니다.
var person = "John Doe", carName = "Volvo", price = 200;
Value = undefined
값 = 정의되지 않다
In computer programs, variables are often declared without a value. The value can be something that has to be calculated, or something that will be provided later, like user input.
A variable declared without a value will have the value undefined.
The variable carName will have the value undefined after the execution of this statement:
컴퓨터 프로그램 안에서는, 변수는 값이 없이 자주 선언됩니다. 계산되어야 하는 값이나 사용자의 입력 같은 것은 나중에 제공하는 것이 가능합니다.
선언한 변수는 값이 없으면 값이 정의되지 않습니다.
명령문을 실행하면 변수 carName의 값이 정의되지 않는 값으로 실행 될 것입니다.
Example var carName;
Re-Declaring JavaScript Variables
자바스크립트 변수를 다시 정의합니다.
If you re-declare a JavaScript variable, it will not lose its value.
The variable carName will still have the value “Volvo” after the execution of these statements:
만약 자바스크립트 변수를 다시선언을 해도 값을 잃어버리진 않을 것 입니다.
변수carName은 계속해서 값으로 “Volvo”를 가지고 문장이 실행 될 것입니다.
Example var carName = "Volvo"; var carName;
JavaScript Arithmetic
자바스크립트 계산
As with algebra, you can do arithmetic with JavaScript variables, using operators like = and +:
당신은 수학처럼 자바스크립트의 변수에 = 와 + 같은 것들로 계산을 하는 것이 가능합니다.
Example var x = 5 + 2 + 3;
You can also add strings, but strings will be concatenated (added end-to-end):
게다가 당신은 문자열을 추가하면 문자열이 연결 됩니다.
Example var x = "John" + " " + "Doe";
Also try this:
이것도 시도해 봅시다.
Example var x = "5" + 2 + 3;
If you add a number to a string, the number will be treated as string, and concatenated.
만약 당신이 숫자에 문자열을 추가하게 된다면, 그 숫자들은 문자열로 취급되어서 연결되어 나오게 됩니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5] [연습문제6]
JavaScript Operators
자바스크립트 연산자
Example Assign values to variables and add them together: var x = 5; // assign the value 5 to x var y = 2; // assign the value 2 to y var z = x + y; // assign the value 7 to z (x + y)
JavaScript Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic on numbers (literals or variables).
연산자의 연산은 (문자 그대로의)숫자를 계산하는데 사용합니다.
Operator Description + Addition 덧셈 - Subtraction 뺄셈 * Multiplication 곱셈 / Division 나눗셈 % Modulus 계수 ++ Increment 증가 -- Decrement 감소 The addition operator (+) adds numbers: 덧셈 연산자는 숫자를 더합니다:
Adding var x = 5; var y = 2; var z = x + y;
The multiplication operator (*) multiplies numbers.
곱셈연산자는 숫자를 곱합니다:
Multiplying var x = 5; var y = 2; var z = x * y;
You will learn more about JavaScript operators in the next chapters.
당신은 더많은 자바스크립트의 연산자에 대해서 다음장에서 배울것 입니다.
JavaScript Assignment Operators
자바스크립트 할당 연산자
Assignment operators assign values to JavaScript variables.
할당 연산자는 자바스크립트의 변수에 값을 할당합니다.
Operator Example Same As = x = y x = y += x += y x = x + y -= x -= y x = x - y *= x *= y x = x * y /= x /= y x = x / y %= x %= y x = x % y The assignment operator (=) assigns a value to a variable. 그할당 연산자는 변수에 값을 = 로 할당합니다. Assignment 할당 var x = 10; The addition assignment operator (+=) adds a value to a variable. 덧셈 할당 연산자는 변수에 값을 더합니다. Assignment 할당 var x = 10; x += 5;
JavaScript String Operators
자바스크립트 문자열 연산자
The + operator can also be used to add (concatenate) strings.
When used on strings, the + operator is called the concatenation operator.
+연산자는 문자열을 더하는데 사용이 가능합니다.
문자열에 +연산자를 사용하면 연결연산자 라고 불립니다.
Example txt1 = "John"; txt2 = "Doe"; txt3 = txt1 + " " + txt2; The result of txt3 will be: txt3에 대한 결과입니다.: John Doe The += assignment operator can also be used to add (concatenate) strings: +=할당 연산자는 문자열을 추가(연결)하여 사용하는게 가능합니다. Example txt1 = "What a very "; txt1 += "nice day"; The result of txt1 will be: txt1에 대한 결과 입니다.: What a very nice day
Adding Strings and Numbers
문자열과 숫자의 덧셈
Adding two numbers, will return the sum, but adding a number and a string will return a string:
두개의 숫자의 합을 반환 하거나, 숫자나와 문자열을 더하면 문자열로 반환합니다.
Example x = 5 + 5; y = "5" + 5; z= "Hello" + 5; The result of x, y, and z will be: x,y,z에 대한 결과입니다: 10 55 Hello5
The rule is: If you add a number and a string, the result will be a string!
규칙 : 만약 당신이 숫자와 문자를 더하면 그 결과는 문자열 입니다!
JavaScript Comparison and Logical Operators
자바스크립트 비교와 논리적인 연산자
Operator Description == equal to 같다 === equal value and equal type 값과 타입이 같다 != not equal 같지 않다 !== not equal value or not equal type 값또는 타입이 같지않다 > greater than 보다 크다 < less than 보다 작다 >= greater than or equal to 보다 크거나 같다 <= less than or equal to 보다 작거나 같다
Comparison and logical operators are described in the JS Comparisons chapter.
비교와 논리적인 연산자는 JS Comparisons장에서 설명하겠습니다.
JavaScript Arithmetic
자바스크립트 계산
A typical thing to do with numbers is arithmetic.
전형적인 숫자 계산 방법
JavaScript Arithmetic Operators
자바스크립트 연산자
Arithmetic operators perform arithmetic on numbers (literals or variables).
계산 연산자는 (상수나 변수)숫자를 계산합니다
Operator Description + Addition 덧셈 - Subtraction 뺄셈 * Multiplication 곱셈 / Division 나눗셈 % Modulus 계수 ++ Increment 증가 -- Decrement 감소
Arithmetic Operations
연산자 계산
A typical arithmetic operation operates on two numbers.
The two numbers can be literals:
전형적인 계산을 진행할 때는 두개의 숫자로 진행합니다.
두개의 상수로 가능합니다
Example var x = 100 + 50;
or variables: 또는 변수로
Example var x = a + b;
or expressions: 다른 식
Example var x = (100 + 50) * a;
Operators and Operands
피연산자 와 연산자
The numbers (in an arithmetic operation) are called operands.
The operation (to be performed between the two operands) is defined by an operator.
숫자(연산)는 피연산자 라고 불려집니다.
(두 피연산자 사이에 실행될)동작을 연산자로 정의합니다.
Operands Operators Operand 100 + 50
The addition operator (+) adds numbers:
덧셈 연산자는 숫자를 더합니다.
Adding var x = 5; var y = 2; var z = x + y;
The subtraction operator (-) subtracts numbers.
뺄셈 연산자는 숫자를 뺍니다.
Subtracting var x = 5; var y = 2; var z = x - y;
The multiplication operator (*) multiplies numbers.
곱셈 연산자는 숫자를 곱합니다.
Multiplying var x = 5; var y = 2; var z = x * y;
The division operator (/) divides numbers.
나눗셈 연산자는 숫자를 나눕니다.
Dividing var x = 5; var y = 2; var z = x / y;
The modular operator (%) returns the division remainder.
모듈러 연산자는 분할된 나머지를 반환합니다.
Modulus var x = 5; var y = 2; var z = x % y;
The increment operator (++) increments numbers.
증가 연산자는 숫자를 증가시킵니다.
Incrementing var x = 5; x++; var z = x;
The decrement operator (- -) decrements numbers.
감소 연산자는 숫자를 감소시킵니다.
Decrementing var x = 5; x--; var z = x;
Operator Precedence
연산자 순서
Operator precedence describes the order in which operations are performed in an arithmetic expression.
연산자 우선순위에 따른 연산 순서에 대해서 설명합니다.
Example var x = 100 + 50 * 3;
Is the result of example above the same as 150 * 3, or is it the same as 100 + 150?
Is the addition or the multiplication done first?
As in traditional school mathematics, the multiplication is done first.
Multiplication (*) and division (/) have higher precedence than addition (+) and subtraction (-).
And (as in school mathematics) the precedence can be changed by using parentheses:
위의 예제와 같은 결과는 150 * 3 또는 100 + 150과 같습니까?
덧셈과 곱셈중 어떤것이 먼저일까?
전형적인 학교 수학에서는, 곱셈을 먼저 합니다.
곱셈과 나눗셈은 덧셈과 뺄셈보다 우선 순위 입니다.
그리고 학교 수학에서처럼 괄호로 우선순위를 바꿀 수 있습니다.
Example var x = (100 + 50) * 3;
When using parentheses, the operations inside the parentheses are computed first.
When many operations have the same precedence (like addition and subtraction), they are computed from left to right:
괄호를 사용할때, 연산자는 괄호 안을 먼저 계산을 합니다.
덧셈과 뺄셈처럼 연산의 우선순위가 같을경우에는 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 계산합니다.
Example var x = 100 + 50 - 3;
JavaScript Operator Precedence Values
자바스크립트 연산자 값의 우선순위
Value Operator Description Example 19 ( ) Expression grouping (3 + 4) 18 . Member person.name 18 [] Member person["name"] 17 () Function call myFunction() 17 new Create new Date() 16 ++ Postfix Increment i++ 16 -- Postfix Decrement i-- 15 ++ Prefix Increment ++i 15 -- Prefix Decrement --i 15 ! Logical not !(x==y) 15 typeof Type typeof x 14 * Multiplication 10 * 5 14 / Division 10 / 5 14 % Modulo division 10 % 5 14 ** Exponentiation 10 ** 2 13 + Addition 10 + 5 13 - Subtraction 10 - 5 12 << Shift left x << 2 12 >> Shift right x >> 2 11 < Less than x < y 11 <= Less than or equal x <= y 11 > Greater than x > y 11 >= Greater than or equal x >= y 10 == Equal x == y 10 === Strict equal x === y 10 != Unequal x != y 10 !== Strict unequal x !== y 6 && And x && y 5 || Or x || y 3 = Assignment x = y 3 += Assignment x += y 3 -= Assignment x -= y 3 *= Assignment x *= y 3 /= Assignment x /= y
Expressions in parentheses are fully computed before the value is used in the rest of the expression.
다른 식을 계산하기 전에 괄호를 완전히 계산하고 나머지 식을 계산합니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5]
JavaScript Assignment
자바스크립트 할당
JavaScript Assignment Operators
자바스크립트 할당 연산자
Assignment operators assign values to JavaScript variables.
할당 연산자는 자바스크립트 변수에 값을 할당합니다.
Operator Example Same As = x = y x = y += x += y x = x + y -= x -= y x = x - y *= x *= y x = x * y /= x /= y x = x / y %= x %= y x = x % y
The = assignment operator assigns a value to a variable.
=할당 연산자로 변수에 값을 할당합니다.
Assignment var x = 10;
The += assignment operator adds a value to a variable.
+=할당 연산자는 변수에 값을 추가하여 할당합니다.
Assignment var x = 10; x += 5;
The -= assignment operator subtracts a value from a variable.
-=할당 연산자는 변수에 값을 뺄셈하여 할당합니다.
Assignment var x = 10; x -= 5;
The *= assignment operator multiplies a variable.
*=할당 연산자는 변수를 곱합니다.
Assignment var x = 10; x *= 5;
The /= assignment divides a variable.
/=할당 연산자는 변수를 나눕니다.
Assignment var x = 10; x /= 5;
The %= assignment operator assigns a remainder to a variable.
%=할당 연산자는 변수에 나머지 값을 할당합니다.
Assignment var x = 10; x %= 5;
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5]
JavaScript Data Types
자바스크립트 데이터 형식
String, Number, Boolean, Array, Object.
문자열, 숫자, 논리형, 배열, 객체
JavaScript Data Types
자바스크립트 데이터 형식
JavaScript variables can hold many data types: numbers, strings, arrays, objects and more:
자바스크립트 변수들은 많은 데이터 형식들을 가지고 있습니다: 숫자, 문자열, 배열, 객체 와 더많은 것을
var length = 16; // Number
var lastName = "Johnson"; // String
var cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"]; // Array
var x = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe"}; // Object
The Concept of Data Types.
데이터 형식의 개념
In programming, data types is an important concept.
To be able to operate on variables, it is important to know something about the type.
Without data types, a computer cannot safely solve this:
프로그램에서는 데이터형식의 개념이 중요합니다.
변수를 동작할 수 있는, 어떤 유형에 대한 데이터 타입을 아는것이 중요합니다.
데이터 타입이 없이는, 컴퓨터는 안전하게 그것을 해결할 수 없습니다.
var x = 16 + "Volvo";
Does it make any sense to add “Volvo” to sixteen? Will it produce an error or will it produce a result?
JavaScript will treat the example above as:
“Volvo”에 16을 추가한다는 것이 감이 오시나요? 그것은 에러를 발생시키거나 어떤 결과를 만들어 내나요?
자바스크립트 위에 예제를 다음과 같이 처리합니다.
var x = "16" + "Volvo";
When adding a number and a string, JavaScript will treat the number as a string.
자바스크립트는 문자열과 숫자열을 더하면 숫자를 문자로 처리합니다.
Example var x = 16 + "Volvo"; Example var x = "Volvo" + 16;
JavaScript evaluates expressions from left to right. Different sequences can produce different results:
자바스크립트 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 식을 평가합니다. 연속적인다른 순서는 다른 결과를 만들어 냅니다.
JavaScript: var x = 16 + 4 + "Volvo"; Result: 20Volvo JavaScript: var x = "Volvo" + 16 + 4; Result: Volvo164
In the first example, JavaScript treats 16 and 4 as numbers, until it reaches “Volvo”.
In the second example, since the first operand is a string, all operands are treated as strings.
“Volvo”까지 도달하는 첫번째 예제는, 자바스크립트는 16부터 4까지는 숫자로 다루어 집니다.
두번째 예제는, 첫번째에서 문자열을 연산하면은, 모두 문자열로 다루어 집니다.
JavaScript Has Dynamic Types
자바스크립트는 동적인 형식을 가지고 있습니다.
JavaScript has dynamic types. This means that the same variable can be used as different types:
자바스크립트는 동적인 형식을 가지고 있습니다. 이 의미는 변수에 다른 형식을 사용할 수 있다는 것을 의미합니다.
Example var x; // Now x is undefined var x = 5; // Now x is a Number var x = "John"; // Now x is a String
JavaScript Strings
자바스크립트 문자열
A string (or a text string) is a series of characters like “John Doe”.
Strings are written with quotes. You can use single or double quotes:
“John Doe”와 같은 문자열(또는 문자) 입니다.
문자열은 따옴표를 사용합니다. 당신은 따옴표나 쌍따옴표를 사용합니다.
Example var carName = "Volvo XC60"; // Using double quotes var carName = 'Volvo XC60'; // Using single quotes
You can use quotes inside a string, as long as they don’t match the quotes surrounding the string:
당신은 따옴표 안의 문자열과 문자열 주변의 따옴표가 다르기만 하면 그것들을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example var answer = "It's alright"; // Single quote inside double quotes var answer = "He is called 'Johnny'"; // Single quotes inside double quotes var answer = 'He is called "Johnny"'; // Double quotes inside single quotes
You will learn more about strings later in this tutorial.
당신은 다음 튜토리얼에서 더많은 문자열에 대해서 배울 것 입니다.
JavaScript Numbers
자바스크립트 숫자
JavaScript has only one type of numbers.
Numbers can be written with, or without decimals:
자바스크립트는 형식중 하나로 숫자가 있습니다.
숫자는 소수점이 없는것과 있는것으로 사용이 가능합니다.:
Example var x1 = 34.00; // Written with decimals var x2 = 34; // Written without decimals
Extra large or extra small numbers can be written with scientific (exponential) notation:
더 크거나, 작은 숫자들은 (지수)로 표기하는 방법을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example var y = 123e5; // 12300000 var z = 123e-5; // 0.00123
You will learn more about numbers later in this tutorial.
다음 튜토리얼에서 더많은 숫자에 대해서 배울 것 입니다.
JavaScript Booleans
자바스크립트 논리형
Booleans can only have two values: true or false.
Booleans는 true 또는 false의 2개의 값만 가지고 있습니다.
Example var x = true; var y = false;
Booleans are often used in conditional testing.
You will learn more about conditional testing later in this tutorial.
Booleans는 흔히 조건부 테스트 할때 사용됩니다.
당신은 다음 튜토리얼에서 더많은 조건부 테스트에 대해서 배우게 될 것 입니다.
JavaScript Arrays
자바스크립트 배열
JavaScript arrays are written with square brackets.
Array items are separated by commas.
The following code declares (creates) an array called cars, containing three items (car names):
자바스크립트 배열은 대괄호로 사용합니다.
배열의 항목들은 콤마로 구분합니다.
다음으로 나오는 코드는 car로 불리는 배열을 선언하여 만들 것 이고, 3개의 항목 (차이름)이 들어가 있습니다.
Example var cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"];
Array indexes are zero-based, which means the first item is [0], second is [1], and so on.
You will learn more about arrays later in this tutorial.
배열의 인덱스는 첫번째 항목은[0]이고 두번째는[1]로 0을 기반으로 합니다.
당신은 다음 튜토리얼에서 더많은 배열에 대해서 배우게 될 것 입니다.
JavaScript Objects
자바스크립트 객체
JavaScript objects are written with curly braces.
Object properties are written as name:value pairs, separated by commas.
자바스크립트 객체는 중괄호를 사용합니다.
객체는 객체의 속성에 대한 이름:값을 구분할때는 콤마를 사용합니다.
Example
var person = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe", age:50, eyeColor:"blue"};
The object (person) in the example above has 4 properties: firstName, lastName, age, and eyeColor.
You will learn more about objects later in this tutorial.
위 예제에서 객체는 4개의 속성을 가지고 있습니다: firstName, lastName, age, and eyeColor.
당신은 다음 튜토리얼에서 더많은 객체에 대해서 배우게 될 것 입니다.
The typeof Operator
연산자 형식
You can use the JavaScript typeof operator to find the type of a JavaScript variable:
당신은 자바스크립트 연산자 형식으로 자바스크립트 변수에 다음과 같은 형식을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example
typeof "John" // Returns string
typeof 3.14 // Returns number
typeof false // Returns boolean
typeof [1,2,3,4] // Returns object
typeof {name:'John', age:34} // Returns object
In JavaScript, an array is a special type of object. Therefore typeof [1,2,3,4] returns object.
자바스크립트에서 배열은 특별한 물체의 형태 입니다. 그러므로 [1,2,3,4]는 객체 형식으로 반환합니다.
Undefined
정의되지않은
In JavaScript, a variable without a value, has the value undefined. The typeof is also undefined.
자바스크립트에서는 변수에 값이 없으면, 값으로 undefined를 가지고 있습니다. 그것의 형식 또한 undefined입니다.
Example var person; // Value is undefined, type is undefined
Any variable can be emptied, by setting the value to undefined. The type will also be undefined.
어떤 변수이든 undefined로 설정하여 값을 비울 수 있습니다. 그것의 형식 또한 undefined입니다.
Example person = undefined; // Value is undefined, type is undefined
Empty Values
비어있는 값
An empty value has nothing to do with undefined.
An empty string variable has both a value and a type.
빈값은 undefined와 관련이 없습니다.
빈값은 값과 형식 둘다 가지고 있는 문자열 변수 입니다.
Example var car = ""; // The value is "", the typeof is string
Null
가치없는
In JavaScript null is “nothing”. It is supposed to be something that doesn’t exist.
Unfortunately, in JavaScript, the data type of null is an object.
You can consider it a bug in JavaScript that typeof null is an object. It should be null.
You can empty an object by setting it to null:
자바스크립트에서 null은 아무런 의미가 없습니다. 그것은 존재하지 않는 무언가가 될 것입니다.
불행하게도, null의 데이터 형식은 자바스크립트의 객체입니다.
당신은 null형식이 객체인 자바스크립트 문제라고 할 수 있습니다. 그것은 null이 되야합니다.
당신은 null로 객체를 비울 수 있습니다.
Example var person = null; // Value is null, but type is still an object
You can also empty an object by setting it to undefined:
당신은 undefined로 객체를 비울 수 있습니다.
Example var person = undefined; // Value is undefined, type is undefined
Difference Between Undefined and Null
undefined 와 Null의 차이점
typeof undefined // undefined typeof null // object null === undefined // false null == undefined // true
JavaScript functions
자바스크립트 함수
A JavaScript function is a block of code designed to perform a particular task.
A JavaScript function is executed when “something” invokes it (calls it).
자바스크립트 함수는 특정 과제를 수행하는데 필요한 코드 블록입니다.
무언가를 호출할때 자바스크립트 기능을 호출하여 실행합니다.
Example
function myFunction(p1, p2) {
return p1 * p2; // The function returns the product of p1 and p2
}
JavaScript Function Syntax
자바스크립트 함수 문법
A JavaScript function is defined with the function keyword, followed by a name, followed by parentheses ().
Function names can contain letters, digits, underscores, and dollar signs (same rules as variables).
The parentheses may include parameter names separated by commas: (parameter1, parameter2, …)
The code to be executed, by the function, is placed inside curly brackets: {}
자바스크립트 함수는 함수 키워드가 같이 정의 되며 뒤에 이름이 오고, 뒤에 괄호()가 옵니다.
함수 이름은 문자 숫자 밑줄 달러 기호를 포함 할 수 있습니다.
괄호는 쉼표로 구분 된 매개 변수 이름을 포함 할 수 있습니다.
이 코드는 함수에 의해 실행되는, 중괄호 내부에{} 배치됩니다.
function name(parameter1, parameter2, parameter3) {
code to be executed
}
Function parameters are the names listed in the function definition.
Function arguments are the real values received by the function when it is invoked.
Inside the function, the arguments behave as local variables.
A Function is much the same as a Procedure or a Subroutine, in other programming languages.
함수name에 파라미터 명단을 열거합니다.
함수 인수는 값이 호출 될 때 함수에 의해 수신된 실제 값을 받습니다.
함수 내에서 인수는 로컬 변수 처럼 행동합니다.
다른 프로그래밍 언어의 프로시저 또는 서브 루틴과 동일합니다.
Function Invocation
함수 호출
The code inside the function will execute when “something” invokes (calls) the function:
- When an event occurs (when a user clicks a button)
- When it is invoked (called) from JavaScript code
- Automatically (self invoked)
You will learn a lot more about function invocation later in this tutorial.
함수안의 코드가 실행될수 있도록 호출되는 기능:
- 이벤트 발생(사용자가 버튼을 클릭했을 때)
- 자바스크립트 코드에서 호출될 때
- 자동(스스로 호출)
나중에 튜토리얼에서 함수 호출에 대해서 더 많이 배울 것입니다.
Function Return
함수 반환
When JavaScript reaches a return statement, the function will stop executing.
If the function was invoked from a statement, JavaScript will “return” to execute the code after the invoking statement.
Functions often compute a return value. The return value is “returned” back to the “caller”:
자바스크립트에 도달하면 return문은 함수의 실행을 중지합니다.
함수가 호출된 경우에 자바스크립트 호출 문 다음 코드를 실행하기 위해 반환 합니다.
함수들은 계산 리턴 값을 반환 값은 다시 caller를 반환 합니다.
함수는 종종 리턴값을 계산합니다. 반환되어 돌아온 값은 caller 입니다.
Example
Calculate the product of two numbers, and return the result:
두 수의 곱을 계산해서 리턴한 결과 입니다:
var x = myFunction(4, 3); // Function is called, return value will end up in x
function myFunction(a, b) {
return a * b; // Function returns the product of a and b
}
The result in x will be:
x의 결과입니다:
12
Why Functions?
함수는 어떻게 사용할 수 있나요?
You can reuse code: Define the code once, and use it many times.
You can use the same code many times with different arguments, to produce different results.
당신은 코드를 재사용 할 수 있습니다. 한번 코드를 정의하고 그리고 여러번 사용 할 수 있습니다.
당신은 같은 코드를 다른 곳에 사용 하여 다른 결과를 나오게 할 수 있습니다.
Example
Convert Fahrenheit to Celsius:
function toCelsius(fahrenheit) {
return (5/9) * (fahrenheit-32);
}
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = toCelsius(77);
The () Operator Invokes the Function
()연산자 함수 호출
Using the example above, toCelsius refers to the function object, and toCelsius() refers to the function result.
위의 예제를 사용하면, toCelsius는 함수 객체를 참조하고, toCelsius()은 함수 결과를 의미합니다.
Example
Accessing a function without () will return the function definition:
함수에 ()없이 반환하는 함수의 정의입니다.
function toCelsius(fahrenheit) {
return (5/9) * (fahrenheit-32);
}
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = toCelsius;
Functions Used as Variables
변수로 사용 가능한 함수
In JavaScript, you can use functions the same way as you use variables.
당신이 자바스크립트에서 변수를 사용해서, 다음과 같은방식으로 기능을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example You can use: var text = "The temperature is " + toCelsius(77) + " Celsius"; Instead of: var x = toCelsius(32); var text = "The temperature is " + x + " Celsius";
You will learn a lot more about functions later in this tutorial.
나중에 튜토리얼에서 기능에 대한 더 많은 것을 배울 것 입니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5]
JavaScript Objects
자바스크립트 객체
Real Life Objects, Properties, and Methods
현실 객체의 성질과 방법
In real life, a car is an object.
A car has properties like weight and color, and methods like start and stop:
현실 안에서의 객체는 차입니다.
차는 색상과 무게와 같은 성질이 있으며 방법으로는 시작과 정지가 있습니다:
Object:

Properties Methods car.name = Fiat car.start() car.model = 500 car.drive() car.weight = 850kg car.brake() car.color = white car.stop()
All cars have the same properties, but the property values differ from car to car.
All cars have the same methods, but the methods are performed at different times.
모든 차들은 같은 성질을 가지고 있습니다, 하지만 차들은 서로다른 값들을 가지고 있습니다.
모든 차들은 같은 방법을 가지고 있습니다, 하지만 행동을 하는 시간을 다릅니다.
JavaScript Objects
자바스크립트 객체
You have already learned that JavaScript variables are containers for data values.
This code assigns a simple value (Fiat) to a variable named car:
당신은 이미 자바스크립트의 변수는 값들의 컨테이너라는 것을 배웠습니다.
이 코드는 차라는 변수에 차 이름값을 할당한 것 입니다:
var car = "Fiat";
Objects are variables too. But objects can contain many values.
This code assigns many values (Fiat, 500, white) to a variable named car:
객체도 변수 입니다. 하지만 객체는 그안에 많은 값들이 들어가는게 가능합니다.
이 코드는 많은 차 이름에 대한 값들을 지정합니다.
var car = {type:"Fiat", model:500, color:"white"};
The values are written as name:value pairs (name and value separated by a colon).
JavaScript objects are containers for named values.
이름:값 쌍으로 쓰여지면서 많은 값들이 들어가는 것이 가능합니다.
자바스크립트 객체에 이름과 값들이 들어갑니다.
Object Properties
객체의 특성
The name:values pairs (in JavaScript objects) are called properties.
특성으로는 이름 : 값 쌍으로 (자바스크립트 객체안에서)불리어 집니다.
var person = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe", age:50, eyeColor:"blue"};
Property Property Value firstName John lastName Doe age 50 eyeColor blue
Object Methods
객체 방법
Methods are actions that can be performed on objects.
Methods are stored in properties as function definitions.
개체에서 수행할 수 있는 방법 입니다.
방법 함수 정의로 속성에 저장됩니다.
Property Property Value
firstName John
lastName Doe
age 50
eyeColor blue
fullName function() {return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;}
JavaScript objects are containers for named values (called properties) and methods.
자바스크립트 객체는 이름 값과 방법을 담는 컨테이너 입니다.
Object Definition
객체의 정의
You define (and create) a JavaScript object with an object literal:
당신이 만든 자바스크립트 객체는 객체 그대로를 정의합니다.
Example
var person = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe", age:50, eyeColor:"blue"};
Spaces and line breaks are not important. An object definition can span multiple lines:
객체안에서는 줄바꿈이 중요하지 않습니다. 객체는 여러줄에서 정의 될 수도 있습니다.
Example
var person = {
firstName:"John",
lastName:"Doe",
age:50,
eyeColor:"blue"
};
Accessing Object Properties
개체 속성 접근
You can access object properties in two ways:
당신이 객체 속성에 접근하는 방법으로는 2가지가 있습니다.
objectName.propertyName or objectName["propertyName"] Example1 person.lastName; Example2 person["lastName"];
Accessing Object Methods
객체 메소드 접근
You access an object method with the following syntax:
다음으로는 당신이 객체의 메소드에 접근할수 있는 문법 입니다.
objectName.methodName() Example name = person.fullName();
If you access the fullName property, without (), it will return the function definition:
만약 당신이 fullName속성에 ()없이 접근 하면 함수의 정의가 반환될 것입니다.
Example name = person.fullName;
Do Not Declare Strings, Numbers, and Booleans as Objects!
객체에 문자열, 숫자, Booleans를 선언하지 않습니다.
When a JavaScript variable is declared with the keyword “new”, the variable is created as an object:
자바스크립트 변수가 키워드로 선언 된 경우에는 새로운 변수가 만들어 집니다.
var x = new String(); // Declares x as a String object var y = new Number(); // Declares y as a Number object var z = new Boolean(); // Declares z as a Boolean object
Avoid String, Number, and Boolean objects. They complicate your code and slow down execution speed.
You will learn more about objects later in this tutorial.
문자열, 숫자 및 Boolean를 피해야합니다. 그것들은 당신의 코드를 복잡하고 실행 속도를 향상 시킵니다.
당신은 튜토리얼에서 더많은 객체에 대해서 배우게 될 것 입니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
JavaScript Scope
자바스크립트의 범위
Scope is the set of variables you have access to.
당신이 접근할 변수의 범위의 집합
JavaScript Scope
자바스크립트의 범위
In JavaScript, objects and functions are also variables.
In JavaScript, scope is the set of variables, objects, and functions you have access to.
JavaScript has function scope: The scope changes inside functions.
자바스크립트 안에서 객체와 함수 또한 변수 입니다.
자바스크립트에서 범위란 변수, 함수, 객체에 접근하는 집합 입니다.
자바스크립트 함수의 범위 : 함수 안에서 범위를 변경합니다.
Local JavaScript Variables
자바스크립트 지역 변수
Variables declared within a JavaScript function, become LOCAL to the function.
Local variables have local scope: They can only be accessed within the function.
자바스크립트 함수 안에서 선언된 변수는 함수의 지역이 됩니다.
지역 함수가 가지는 범위: 그들은 오직 함수 안에서만 접근 할 수 있습니다
Example
// code here can not use carName
function myFunction() {
var carName = "Volvo";
// code here can use carName
}
Since local variables are only recognized inside their functions, variables with the same name can be used in different functions.
Local variables are created when a function starts, and deleted when the function is completed.
이후에 지역변수는 그것들의 기능안에서 인정되고 있어서 이름이 같은 변수도 다른 기능에 사용 될 수 있습니다.
함수가 시작할 때 지역함수가 생성되었을 때 함수가 완료될 때 삭제 합니다.
Global JavaScript Variables
자바스크립트 전역 변수
A variable declared outside a function, becomes GLOBAL.
A global variable has global scope: All scripts and functions on a web page can access it.
함수 밖에서 선언되어 지면 전역 변수라고 불립니다.
전역 변수는 전체 범위를 가집니다: 전체 웹 페이지의 스크립트와 함수에 접근 할 수 있습니다.
Example
var carName = " Volvo";
// code here can use carName
function myFunction() {
// code here can use carName
}
Automatically Global
전역 자동화
If you assign a value to a variable that has not been declared, it will automatically become a GLOBAL variable.
This code example will declare carName as a global variable, even if it is executed inside a function.
만약 당신이 변수를 선언하지 않고 값을 할당할 경우에 그것은 전역으로 자동화가 될 것입니다.
이 예제 코드는 함수 안에서 실행 되더라도 전역 변수carName으로 선언 될 것 입니다.
Example
// code here can use carName
function myFunction() {
carName = "Volvo";
// code here can use carName
}
The Lifetime of JavaScript Variables
자바스크립트 변수의 수명
The lifetime of a JavaScript variable starts when it is declared.
Local variables are deleted when the function is completed.
Global variables are deleted when you close the page.
자바스크립트 변수를 선언할 때 수명이 시작 됩니다.
지역 변수는 함수가 완료 될 때 삭제 됩니다.
전역 변수는 당신의 페이지를 닫을 때 삭제 됩니다.
Function Arguments
함수의 인수
Function arguments (parameters) work as local variables inside functions.
함수의 인수(파라미터)는 함수 안에서 지역 변수로 실행 합니다.
Global Variables in HTML
HTML안에 전역변수
With JavaScript, the global scope is the complete JavaScript environment.
In HTML, the global scope is the window object: All global variables belong to the window object.
자바스크립트와 같이 전역 범위에 자바스크립트 환경이 완료 됩니다.
HTML에서 윈도우 객체의 전역 범위: 모든 전역 변수는 윈도우 객체에 속합니다.
Example
// code here can use window.carName
function myFunction() {
carName = "Volvo";
}
Did You Know?
당신은 알고 있나요?
Your global variables (or functions) can overwrite window variables (or functions).
Any function, including the window object, can overwrite your global variables and functions.
당신의 전역 변수(또는 함수)는 윈도우 변수(또는 함수)로도 중복하여 사용이 가능합니다.
윈도우 객체를 포함한 함수는 당신의 전역 변수와 함수를 중복하여 사용할 수 있습니다.
JavaScript Events
자바스크립트 이벤트
HTML events are “things” that happen to HTML elements.
When JavaScript is used in HTML pages, JavaScript can “react” on these events.
HTMl이벤트는 HTML요소에서 일어나게 됩니다.
HTML페이지에서 자바스크립트를 사용할 때, 자바스크립트는 그것에 대한 일이 일어나게 됩니다.
HTML Events
HTML 이벤트
An HTML event can be something the browser does, or something a user does. Here are some examples of HTML events:
HTML이벤트는 어떤 브라우저 에서 일어나거나, 사용자에 의해서 일어나게 됩니다.
여기에 HTML이벤트에 대한 약간의 에제가 있습니다:
- An HTML web page has finished loading
- An HTML input field was changed
-
An HTML button was clicked
- HTML 웹 페이지의 로드가 완료
- HTML 필드 입력 변경
- HTML 버튼을 클릭
Often, when events happen, you may want to do something.
JavaScript lets you execute code when events are detected.
HTML allows event handler attributes, with JavaScript code, to be added to HTML elements.
종종 당신은 많은 이벤트 들을 하기를 원합니다.
자바스크립트 이벤트를 감지하여 코드를 실행 할 수 있습니다.
HTML이벤트 핸들러가 있는 HTML요소를 자바스크립트 코드에 추가합니다.
With single quotes: 따옴표 <some-HTML-element some-event='some JavaScript'> With double quotes: 쌍따옴표 <some-HTML-element some-event="some JavaScript">
In the following example, an onclick attribute (with code), is added to a button element:
다음 예제에서는 클릭 속성을 엘리먼트 버튼에 추가하는 것 입니다.
Example
<button onclick='getElementById("demo").innerHTML=Date()'>The time is?</button>
In the example above, the JavaScript code changes the content of the element with id=”demo”.
In the next example, the code changes the content of its own element (using this.innerHTML):
위의 예제에서는 자바스크립트 코드에서 id=”demo”와 요소를 바꾸는 것 이였습니다.
다음 예제 코드는 자신의 요소를(this.innerHTML을 사용하여)내용을 바꿉니다.
Example <button onclick="this.innerHTML=Date()">The time is?</button>
JavaScript code is often several lines long. It is more common to see event attributes calling functions:
Example <button onclick="displayDate()">The time is?</button>
Common HTML Events
일반적인 HTML이벤트
Here is a list of some common HTML events:
여기에 일반적인 HTML이벤트에대한 목록이 있습니다:
Event Description onchange An HTML element has been changed onclick The user clicks an HTML element onmouseover The user moves the mouse over an HTML element onmouseout The user moves the mouse away from an HTML element onkeydown The user pushes a keyboard key onload The browser has finished loading the page 이벤트 설명 onchange HTML요소가 변경됩니다. onclick 사용자의 HTML요소를 클릭하면 onmouseover 사용자가 요소위에 마우스를 이동시키면 onmouseout 사용자가 요소에서 다른곳으로 마우스를 이동시키면 onkeydown 사용자가 키보드를 누르면 onload 브라우저 페이지 로딩이 끝나면
The list is much longer: W3Schools JavaScript Reference HTML DOM Events.
이목록 보다 더많은 내용: W3Schools JavaScript Reference HTML DOM Events.
What can JavaScript Do?
자바스크립트는 무슨일을 할 수 있나요?
Event handlers can be used to handle, and verify, user input, user actions, and browser actions:
이벤트 헨들러는 입력, 동작, 브라우저 동작을 하는데 사용 할 수 있습니다.
- Things that should be done every time a page loads
- Things that should be done when the page is closed
- Action that should be performed when a user clicks a button
- Content that should be verified when a user inputs data
-
And more …
- 페이지 로드가 일어날 때마다 실행됩니다.
- 페이지를 닫을 때마다 실행됩니다.
- 사용자가 버튼을 클릭 할 때 실행 됩니다.
- 사용자가 입력한 데이터내용을 확인 할 때 실행 됩니다.
- 그리고 더 많이…
Many different methods can be used to let JavaScript work with events:
많은 다른 방법으로 이벤트와 자바스크립트 작업을 할 수 있습니다.
- HTML event attributes can execute JavaScript code directly
- HTML event attributes can call JavaScript functions
- You can assign your own event handler functions to HTML elements
- You can prevent events from being sent or being handled
-
And more …
- HTML이벤트 속성에서 직접 자바스크립트 코드를 실행 할 수 있습니다.
- HTML이벤트 속성은 자바스크립트 함수를 호출 할 수 있습니다.
- 당신은 HTML요소로 자신의 이벤트 핸들러 기능을 할당 할 수 있습니다
- 당신은 전송되는 처리 이벤트를 방지 할 수 있습니다.
- 그리고 더 많이…
You will learn a lot more about events and event handlers in the HTML DOM chapters.
당신은 HTML DOM장에서 더많은 이벤트와 이벤트 핸들러에 대해서 배우게 될 것 입니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
JavaScript Strings
자바스크립트 문자열
JavaScript strings are used for storing and manipulating text.
자바스크립트 문자열은 text를 저장하거나 처리할 때 사용합니다.
JavaScript Strings
자바스크립트 문자열
A JavaScript string simply stores a series of characters like “John Doe”.
A string can be any text inside quotes. You can use single or double quotes:
자바스크립트 문자열은 “John Doe”와 비슷하게 문자로 저장합니다.
문자열은 당신의 작은 따옴표나 큰 따옴표 부호안에다가 텍스트를 넣어서 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example var carname = "Volvo XC60"; var carname = 'Volvo XC60';
You can use quotes inside a string, as long as they don’t match the quotes surrounding the string:
문자열을 둘러싼 따옴표와 다른 종류의 따옴표를 문자열 안에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example var answer = "It's alright"; var answer = "He is called 'Johnny'"; var answer = 'He is called "Johnny"';
String Length
문자열 길이
The length of a string is found in the built in property length:
문자열의 길이는 속성의 길이 안에서 만들어진 것 중에서 찾는다.
Example var txt = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; var sln = txt.length;
Special Characters
특수문자
Because strings must be written within quotes, JavaScript will misunderstand this string:
문자열은 따옴표안에서 써야하기 때문에 자바스크립트는 이 문자열을 오해합니다.
var y = "We are the so-called "Vikings" from the north."
The string will be chopped to “We are the so-called “.
The solution to avoid this problem, is to use the \ escape character.
The backslash escape character turns special characters into string characters:
문자열을 “We are the so-called “로 개조 해야합니다.
이것의 해결방법은 \를 사용해서 문자를 확장시켜서 문제를 방지해야 합니다.
역슬래시는 문자는 문자열안에서의 특수문자를 되돌려줍니다.
Example var x = 'It\'s alright'; var y = "We are the so-called \"Vikings\" from the north."
The escape character () can also be used to insert other special characters in a string.
This is the list of special characters that can be added to a text string with the backslash sign:
이스케이프 문자()는 문자열에 다른 특수문자를 넣을 수 있습니다.
역슬래시 기호에 문자를 쓰면 문자열에 추가할 수 있는 특수 문자의 목록 입니다.
Code Outputs \' single quote \" double quote \\ backslash \n new line \r carriage return \t tab \b backspace \f form feed
Breaking Long Code Lines
긴코드의 줄바꿈
For best readability, programmers often like to avoid code lines longer than 80 characters.
If a JavaScript statement does not fit on one line, the best place to break it is after an operator:
최고의 가독성을 위해서 프로그래머는 흔히 80문자보다 긴 코드를 피해야 합니다.
자바스크립트문장에서 한줄에 다 표시할 수 없을 경우에 줄을 바꾸기 위한 최고의 장소는 연산자 입니다.
Example
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML =
"Hello Dolly.";
You can also break up a code line within a text string with a single backslash:
당신은 코드 라인을 text문자열 안에서 \로 라인을 분리할 수 있습니다.
Example
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Hello \
Dolly!";
The \ method is not a ECMAScript (JavaScript) standard.
Some browsers do not allow spaces behind the \ character.
\방법은 스크립트 표준 방법이 아닙니다.
일부의 브라우저에서는 \문자 뒤에 공백을 허용하지 않습니다.
The safest (but a little slower) way to break a long string is to use string addition:
가장 안정적인 긴 문장에서의 줄바꿈은 문자열을 추가하여 줄바꿈 하는 방법입니다.
Example
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = "Hello" +
"Dolly!";
You cannot break up a code line with a backslash:
당신은 백슬래시 코드로도 문장을 분리 할 수 있습니다.
Example
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = \
"Hello Dolly!";
Strings Can be Objects
객체로 문자열 사용이 가능합니다
Normally, JavaScript strings are primitive values, created from literals: var firstName = “John”
But strings can also be defined as objects with the keyword new: var firstName = new String(“John”)
보통, 자바스크립트 문자열은 상수를 만들때 var firstName = “John”로 만듭니다.
하지만 문자열은 새로운 객체로 정의하여 만들어 낼 수 도 있습니다.var firstName = new String(“John”)
Example
var x = "John";
var y = new String("John");
// typeof x will return string
// typeof y will return object
// x타입은 문자열을 반환한다.
// y타입은 객체를 반환한다.
Don’t create strings as objects. It slows down execution speed, and produces nasty side effects:
객체와 같은 문자열을 만들면 안됩니다. 그것은 실행속도를 느리게하고, 부작용을 만들어낼 수 있습니다.
When using the == equality operator, equal strings looks equal:
동일한 문자열에 대한 비교를 할때에는 ==평등 연산자를 사용합니다.
Example
var x = "John";
var y = new String("John");
// (x == y) is true because x and y have equal values
// x와y는 같은 값을 가지고 있기 때문에 true입니다.
When using the === equality operator, equal strings are not equal, because the === operator expects equality in both type and value.
=== 연산자를 사용할 경우에는, 문자의 값과 타입까지 비교하기때문에, 두 문자열은 동일하지 않습니다.
Example
var x = "John";
var y = new String("John");
// (x === y) is false because x and y have different types (string and object)
// (x === y) x와y는 서로다른 문자열 형식을 가지고 있기때문에 false입니다.
Or even worse. Objects cannot be compared:
더 나쁜 예로는 객체는 비교할 수 없습니다.
Example
var x = new String("John");
var y = new String("John");
// (x == y) is false because x and y are different objects
// (x == x) is true because both are the same object
// x와y는 다른 객체이기 때문에 false입니다.
// x == x는 둘다 같은 객체이기 때문에 true입니다.
JavaScript objects cannot be compared.
자바스크립트 객체는 비교할 수 없습니다.
String Properties and Methods
문자열의 속성과 방법
Primitive values, like “John Doe”, cannot have properties or methods (because they are not objects).
But with JavaScript, methods and properties are also available to primitive values, because JavaScript treats primitive values as objects when executing methods and properties.
기본타입은 속성이나 methods를 가질 수 없습니다.(때문에 그것들은 객체가 아닙니다)
하지만 자바스크립트는 메서드와 속성을 실행할 때 객체로 기본값을 처리하기 때문에 방법이나 속성을 기본타입으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
String methods are covered in next chapter.
문자열 methods는 다음 장에서 설명합니다.
String Properties
문자열 속성
Property Description constructor Returns the function that created the String object's prototype length Returns the length of a string prototype Allows you to add properties and methods to an object
Property Description constructor 함수에 만들어진 문자열 객체의 원형을 반환합니다. length 문자열의 길이를 반환합니다. prototype 당신의 객체에 속성이나 메서드를 추가하는 것을 허용합니다.
String Methods
문자열 methods
Method Description charAt() Returns the character at the specified index (position) charCodeAt() Returns the Unicode of the character at the specified index concat() Joins two or more strings, and returns a copy of the joined strings fromCharCode() Converts Unicode values to characters indexOf() Returns the position of the first found occurrence of a specified value in a string lastIndexOf() Returns the position of the last found occurrence of a specified value in a string localeCompare() Compares two strings in the current locale match() Searches a string for a match against a regular expression, and returns the matches replace() Searches a string for a value and returns a new string with the value replaced search() Searches a string for a value and returns the position of the match slice() Extracts a part of a string and returns a new string split() Splits a string into an array of substrings substr() Extracts a part of a string from a start position through a number of characters substring() Extracts a part of a string between two specified positions toLocaleLowerCase() Converts a string to lowercase letters, according to the host's locale toLocaleUpperCase() Converts a string to uppercase letters, according to the host's locale toLowerCase() Converts a string to lowercase letters toString() Returns the value of a String object toUpperCase() Converts a string to uppercase letters trim() Removes whitespace from both ends of a string valueOf() Returns the primitive value of a String object
Method Description charAt() 지정한 인덱스 위치에 있는 문자열을 반환합니다. charCodeAt() 문자의 유니코드는 지정된 인덱스를 반환합니다. concat() 2개의상의 문자열을 연결하고 연결된 문자열의 복사본을 반환합니다. fromCharCode() 문자를 유니코드값으로 변환합니다. indexOf() 문자열에 저장된 값중에 첫번째 발견된 위치의 값을 반환합니다. lastIndexOf() 문자열에 저장된 값중에 마지막에 발견된 위치의 값을 반환합니다. localeCompare() 현제 위치의 2개의 문자열을 비교합니다. match() 정규식에 일치하는 문자열을 검색하여 일치되는 내용을 반환합니다. replace() 값으로 문자열을 검색하여 대체값을 가지는 새로운 문자열을 반환합니다. search() 문자열 값을 검색하여 일치하는 값을 반환합니다. slice() 문자열의 일부를 추출해서 새로운 문자열로 반환합니다. split() 문자열의 배열로 문자열을 분할합니다. substr() 문자 숫자의 위치로부터 문자열의 일부를 추출합니다. substring() 지정된 두 위치 사이에 문자열의 일부를 추출합니다. toLocaleLowerCase() host's locale에 따라서 소문자 문자열을 반환합니다. toLocaleUpperCase() host's locale에 따라서 대문자 문자열을 반환합니다. toLowerCase() 글자를 소문자 문자열로 변환합니다. toString() string객체의 값을 반환합니다. toUpperCase() 글자를 대문자 문자열로 변환합니다. trim() 문자열의 양쪽 끝의 공백을 제거 합니다. valueOf() 문자열 객체의 기본형식의 값을 반환합니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
JavaScript String Methods
자바스크립트 문자열 Methods
String methods help you to work with strings.
문자열methods는 문자열 작업을 하는데 도움이 됩니다.
Finding a String in a String
문자열에서 문자열 찾기
The indexOf() method returns the index of (the position of) the first occurrence of a specified text in a string:
indexOf()메소드는 첫번째 문자열에서 지정된 문자열이 존재하면 index를 반환합니다.
Example
var str = "Please locate where 'locate' occurs!";
var pos = str.indexOf("locate");
The lastIndexOf() method returns the index of the last occurrence of a specified text in a string:
lastIndexOf()메소드는 문자열에서 마지막에 존재하는 명시된 문자의 index를 반환합니다.
Example
var str = "Please locate where 'locate' occurs!";
var pos = str.lastIndexOf("locate");
Both the indexOf(), and the lastIndexOf() methods return -1 if the text is not found.
indexOf()와 lastIndexOf()메소드 둘다 문자를 찾을 수 없으면 -1을 반환 합니다.
JavaScript counts positions from zero.
0 is the first position in a string, 1 is the second, 2 is the third …
Both methods accept a second parameter as the starting position for the search.
자바스크립트는 0에서부터 수를 셉니다.
0번부터 시작하여 2번째는 1, 3번째는 2 …
두 메소드는 2번째 파라미터로 검색의 시작위치를 받아들입니다.
Searching for a String in a String
문자열에서 문자열 검색
The search() method searches a string for a specified value and returns the position of the match:
search()메소드는 지정된 값으로 문자열을 검색하고 일치하는 위치를 반환합니다.
Example
var str = "Please locate where 'locate' occurs!";
var pos = str.search("locate");
Did You Notice?
당신은 주의 하셨나요?
The two methods, indexOf() and search(), are equal.
They accept the same arguments (parameters), and they return the same value.
The two methods are equal, but the search() method can take much more powerful search values.
You will learn more about powerful search values in the chapter about regular expressions.
indexOf()와 search()두 메소드는 동일합니다.
그들은 같은 인수를 받아들여서 동일한 값을 반환합니다.
두 가지 방법은 같지만 search()메소드는 훨씬 더 효과적으로 값을 검색할 수 있습니다.
당신은 정규 표현식에 대한 장에서 효과적인 검색 값에 대하여 배울 것 입니다.
Extracting String Parts
문자열 부분 추출
There are 3 methods for extracting a part of a string:
문자열의 일부를 추출하기 위한 3가지 방법이 있습니다.
- slice(start, end)
- substring(start, end)
- substr(start, length)
The slice() Method
slice()메소드
slice() extracts a part of a string and returns the extracted part in a new string.
The method takes 2 parameters: the starting index (position), and the ending index (position).
This example slices out a portion of a string from position 7 to position 13:
slice()는 문자열의 일부를 추출하여 새로운 문자열에서 추출된 부분을 반환합니다.
시작 인덱스(위치)와 종료 인덱스(위치)로 2개의 파라미터로 만들어 집니다.
이 예제는 7번 위치에서 13번 이치까지 문자열 부분을 추출한 것 입니다.
Example var str = "Apple, Banana, Kiwi"; var res = str.slice(7,13); The result of res will be: Banana
If a parameter is negative, the position is counted from the end of the string.
This example slices out a portion of a string from +position -12 to position -6:
만약 파라미터가 음수면 문자열 위치의 끝에서부터 카운트 됩니다.
Example var str = "Apple, Banana, Kiwi"; var res = str.slice(-12,-6); The result of res will be: Banana
If you omit the second parameter, the method will slice out the rest of the string:
만약 당신이 2번째 파라미터를 생략하면, 문자열의 나머지를 자를 것 입니다.
Example var res = str.slice(7);
or, counting from the end:
또는 마지막부터 시작
Example var res = str.slice(-12);
Negative positions does not work in Internet Explorer 8 and earlier.
음수는 위치는 Internet Explorer8에서는 동작하지 않습니다.
The substring() Method
문자열()메소드
substring() is similar to slice().
The difference is that substring() cannot accept negative indexes.
substring()과 slice()는 비슷합니다.
차이점은 substring()은 음수 인덱스를 받아들일 수 없다는 것입니다.
Example var str = "Apple, Banana, Kiwi"; var res = str.substring(7,13); The result of res will be: Banana
If you omit the second parameter, substring() will slice out the rest of the string.
만약 두번째 파라미터를 생략하면 substring()은 문자열의 나머지 부분을 잘라냅니다.
The substr() Method
substr()메소드
substr() is similar to slice().
The difference is that the second parameter specifies the length of the extracted part.
substr()은 slice()와 비슷합니다.
두번째 파라미터에 지정된 것은 추출될 부분의 길이 차이 입니다.
Example var str = "Apple, Banana, Kiwi"; var res = str.substr(7,6); The result of res will be: Banana
If the first parameter is negative, the position counts from the end of the string.
The second parameter can not be negative, because it defines the length.
If you omit the second parameter, substr() will slice out the rest of the string.
만약 첫번째 파라미터가 음수면 문자열 끝에서 부터 카운트 합니다.
두번째 파라미터는 문자의 길이를 정의하기 때문에 음수가 올 수 없습니다.
만약 두번째 파라미터를 생략한다면 substr()은 문자열의 나머지 부분을 잘라냅니다.
Replacing String Content
문자열의 내용 교체
The replace() method replaces a specified value with another value in a string:
replace()메소드는 문자열을 지정된 값으로 대체합니다.
Example
str = "Please visit Microsoft!";
var n = str.replace("Microsoft","W3Schools");
The replace() method can also take a regular expression as the search value.
replace()메소드 또한 검색값과 같은 정규식으로 취할 수 있습니다.
Converting to Upper and Lower Case
대소문자 변환
A string is converted to upper case with toUpperCase():
toUpperCase()는 문자열을 대문자로 변환합니다.
Example var text1 = "Hello World!"; // String var text2 = text1.toUpperCase(); // text2 is text1 converted to upper
A string is converted to lower case with toLowerCase():
toLowerCase()는 문자열을 소문자로 변환합니다.
Example var text1 = "Hello World!"; // String var text2 = text1.toLowerCase(); // text2 is text1 converted to lower
The concat() Method
concat() joins two or more strings:
concat() 2개이상의 문자열 연결
Example
var text1 = "Hello";
var text2 = "World";
text3 = text1.concat(" ",text2);
The concat() method can be used instead of the plus operator. These two lines do the same:
concat()메소드로 더하기 연산자를 대신해서 사용할 수 있습니다. 두 라인은 같은 작업을 수행합니다.
Example
var text = "Hello" + " " + "World!";
var text = "Hello".concat(" ","World!");
All string methods return a new string. They don’t modify the original string.
Formally said: Strings are immutable: Strings cannot be changed, only replaced.
모든 문자열 메소드는 새로운 문자열을 반환합니다. 그들은 원래 문자열을 수정하지 않습니다.
공식적으로: 문자열은 불변함으로 변경이나 교체를 할 수 없습니다.
Extracting String Characters
문자열의 문자열 추출
There are 2 safe methods for extracting string characters:
2개의 안전하게 문자열을 추출하는 방법
- charAt(position)
- charCodeAt(position)
The charAt() Method
charAt()메소드
The charAt() method returns the character at a specified index (position) in a string:
charAt()메소드는 문자열에서 지정된 인덱스 위치에 있는 문자를 반환합니다.
Example var str = "HELLO WORLD"; str.charAt(0); // returns H
The charCodeAt() Method
charCodeAt()메소드
The charCodeAt() method returns the unicode of the character at a specified index in a string:
charCodeAt()메소드는 문자열에서 지정된 인덱스에 있는 유니코드를 반환합니다.
Example var str = "HELLO WORLD"; str.charCodeAt(0); // returns 72
Accessing a String as an Array is Unsafe
불안전한 문자열 배열 접근
You might have seen code like this, accessing a string as an array:
당신은 배열로 문자열에 접근하는 이와 같은 코드를 본적이 있습니다.
var str = "HELLO WORLD"; str[0]; // returns H
This is unsafe and unpredictable:
불안전하고 예측할수 없다.
- It does not work in all browsers (not in IE5, IE6, IE7)
- It makes strings look like arrays (but they are not)
-
str[0] = “H” does not give an error (but does not work)
- 그것은 모든 브라우저에서 동작하지 않습니다.
- 그것은 문자열 배열처럼보이게(하지만 그들은 그렇지 않다.)
- str[0] = “H”오류를 제공하지 않습니다(하지만 동작하지 않는다)
If you want to read a string as an array, convert it to an array first.
당신은 배열로 문자열을 읽으려면, 문저배열로 반환해합니다.
Converting a String to an Array
문자열을 배열로 변환
A string can be converted to an array with the split() method:
문자열을 배열로 변환할 수 있습니다 split()방법
Example
var txt = "a,b,c,d,e"; // String
txt.split(","); // Split on commas
txt.split(" "); // Split on spaces
txt.split("|"); // Split on pipe
If the separator is omitted, the returned array will contain the whole string in index [0].
If the separator is “ “, the returned array will be an array of single characters:
만약 구분을 생략하면 반환된 배열 인덱스[0]의 전체 문자열이 포함됩니다.
구분” “의 경우 반환된 배열은 단일 문자의 배열이 될 것입니다.
Example
var txt = "Hello"; // String
txt.split(""); // Split in characters
Complete String Reference
전체 문자열 참조
For a complete reference, go to our Complete JavaScript String Reference.
The reference contains descriptions and examples of all string properties and methods.
필요한 모든 것이 갖춰진 우리 자바스크립트 String reference참조
reference에는 모든 String의 속성과 메소드에 대한 설명과 예제가 들어 있습니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5] [연습문제6]
JavaScript Numbers
자바스크립트 숫자
JavaScript has only one type of number.
Numbers can be written with, or without, decimals.
자바스크립트는 오직 하나의 숫자 타입만 가지고 있습니다.
숫자는 소수점없는 십진법으로 사용합니다.
JavaScript Numbers
자바스크립트 숫자
JavaScript numbers can be written with, or without decimals:
자바스크립트 숫자는 소수점없는 십진법으로 사용이 가능합니다.
Example var x = 34.00; // A number with decimals var y = 34; // A number without decimals
Extra large or extra small numbers can be written with scientific (exponent) notation:
매우 크거나 작은 숫자들은 지수 표기법으로 쓸 수 있습니다.
Example var x = 123e5; // 12300000 var y = 123e-5; // 0.00123
JavaScript Numbers are Always 64-bit Floating Point
자바스크립트는 항상 64비트의 부동 소수점 숫자 입니다.
Unlike many other programming languages, JavaScript does not define different types of numbers, like integers, short, long, floating-point etc.
JavaScript numbers are always stored as double precision floating point numbers, following the international IEEE 754 standard.
This format stores numbers in 64 bits, where the number (the fraction) is stored in bits 0 to 51, the exponent in bits 52 to 62, and the sign in bit 63:
많은 프로그래밍 언어와는 다르게 자바스크립트는 정수, 부동소수점 숫자를 다른유형을 정의하지 않습니다.
자바 스크립트 번호 항상 배정 밀도 부동 소수 점 숫자로, 국제 IEEE754기준에 따르저장됩니다.
이 형식이 숫자(분수)비트에 051에 저장된다 64비트이며, 지수에서 비트에 52로는 62에서, 비트 전송 63에서:번호 저장합니다.
Value (aka Fraction/Mantissa) Exponent Sign 52 bits (0 - 51) 11 bits (52 - 62) 1 bit (63)
Precision
정확성
Integers (numbers without a period or exponent notation) are considered accurate up to 15 digits.
정수는 15자리까지 정확한 것으로 간주됩니다.
Example var x = 999999999999999; // x will be 999999999999999 var y = 9999999999999999; // y will be 10000000000000000
The maximum number of decimals is 17, but floating point arithmetic is not always 100% accurate:
소수의 최대 갯수는 17개 이며 연산은 항상 100% 정확한 것은 아니다
Example var x = 0.2 + 0.1; // x will be 0.30000000000000004
To solve the problem above, it helps to multiply and divide:
문제들을 해결하기 위해서는 곱하기와 나누기로 도와줘야한다.
Example var x = (0.2 * 10 + 0.1 * 10) / 10; // x will be 0.3
Hexadecimal
진수
JavaScript interprets numeric constants as hexadecimal if they are preceded by 0x.
그들은 0x를 시작으로 하느 경우에 자바스크립트 진수로 상수 숫자를 해석 합니다
Example var x = 0xFF; // x will be 255
Never write a number with a leading zero (like 07).
Some JavaScript versions interpret numbers as octal if they are written with a leading zero.
절대로 앞에0 과같은 숫자를 쓰지 마십시오.
그것들은 자바스크립트에서 일부 버전에선 숫자로 해석합니다.
By default, Javascript displays numbers as base 10 decimals.
But you can use the toString() method to output numbers as base 16 (hex), base 8 (octal), or base 2 (binary).
기본적으로 자바스크립트는 10진수로 숫자를 표시합니다.
하지만 당신은 toStirng()메소드에 16진수 2진수 8진수 모두를 사용한 수 있습니다.
Example var myNumber = 128; myNumber.toString(16); // returns 80 myNumber.toString(8); // returns 200 myNumber.toString(2); // returns 10000000
Infinity
무한대
Infinity (or -Infinity) is the value JavaScript will return if you calculate a number outside the largest possible number.
무한대(또는 -무한대)값은 자바스크립트에서 가장 큰 수를 계산하는 것 입니다.
Example
var myNumber = 2;
while (myNumber != Infinity) { // Execute until Infinity
myNumber = myNumber * myNumber;
}
Division by 0 (zero) also generates Infinity:
0으로 나누면 무한대를 발생 시킵니다.
" Example var x = 2 / 0; // x will be Infinity var y = -2 / 0; // y will be -Infinity
Infinity is a number: typeOf Infinity returns number.
무한대는 숫자입니다 : 무한태는 타입으로 숫자를 반환합니다.
Example typeof Infinity; // returns "number"
NaN - Not a Number
NaN은 숫자가 아닙니다
NaN is a JavaScript reserved word indicating that a value is not a number.
Trying to do arithmetic with a non-numeric string will result in NaN (Not a Number):
NaN은 값이 숫자가 아닌것을 나타내는 자바스크립트예약어 입니다.
숫자가 아닌 문자열로 연산하려하면 NaN이 발생합니다.
Example var x = 100 / "Apple"; // x will be NaN (Not a Number)
However, if the string contains a numeric value , the result will be a number:
문자열에 숫자 값이 있는 경우에는 결과로 숫자값이 나올 것입니다.
Example var x = 100 / "10"; // x will be 10
You can use the global JavaScript function isNaN() to find out if a value is a number.
당신은 자바스크립트 함수 isNaN()을 사용해서 값이 숫자인지 알아 볼 수 있습니다
Example var x = 100 / "Apple"; isNaN(x); // returns true because x is Not a Number
Watch out for NaN. If you use NaN in a mathematical operation, the result will also be NaN:
NaN을 조심해야 합니다. 만약 당신이 NaN으로 수학적인 연산을 하면, 결과는 NaN이 될 것입니다.
Example var x = NaN; var y = 5; var z = x + y; // z will be NaN
Or the result might be a concatenation:
아니면 결과는 연결될 수 있습니다.
Example var x = NaN; var y = "5"; var z = x + y; // z will be NaN5
NaN is a number, and typeof NaN returns number:
NaN은 숫자 입니다 그리고 NaN은 타입으로 숫자를 반환합니다
Example typeof NaN; // returns "number"
Numbers Can be Objects
숫자는 객체로도 가능합니다
Normally JavaScript numbers are primitive values created from literals: var x = 123
But numbers can also be defined as objects with the keyword new: var y = new Number(123)
보통의 자바스크립트는 숫자의 원시 값은 리터럴로 만들어 집니다: var x = 123와 같이
하지만 숫자는 var y = new Number(123)와 같이 new 키워드와 객체로 정의할 수 있습니다.
Example var x = 123; var y = new Number(123); // typeof x returns number // typeof y returns object
Don’t create Number objects. It slows down execution speed. The new keyword complicates the code. This can produce some unexpected results:
숫자는 객체를 만들지 않습니다. 이것은 실행 속도가 느려지고 새로운 키워드 코드를 복잡하게 합니다. 이것은 예상하지 못한 결과를 얻을 수 있습니다.
When using the == equality operator, equal numbers looks equal:
== 비교 연산자를 사용하는 경우에는 같은 숫자는 동일합니다
Example var x = 500; var y = new Number(500); // (x == y) is true because x and y have equal values
When using the === equality operator, equal numbers are not equal, because the === operator expects equality in both type and value.
=== 비교 연산자를 사용하는 경우 === 연산자는 유형과 값 모두 같아야 하기 때문에 숫자 값은 같아도 형식은 같지 않습니다.
Example var x = 500; var y = new Number(500); // (x === y) is false because x and y have different types
Or even worse. Objects cannot be compared:
아니면 그밖에도 객체는 비교할 수 없습니다.
Example var x = new Number(500); var y = new Number(500); // (x == y) is false because objects cannot be compared
JavaScript objects cannot be compared.
자바스크립트 객체는 비교할 수 없습니다.
Number Properties and Methods
숫자의 속성과 방법
Primitive values (like 3.14 or 2014), cannot have properties and methods (because they are not objects).
But with JavaScript, methods and properties are also available to primitive values, because JavaScript treats primitive values as objects when executing methods and properties.
기본값(3.14또는2014등) 속성과 방법을 가질 수 없습니다.
하지만 메서드와 속성을 실행할 때 자바스크립트 객체로 기본 값을 처리하기 때문에 자바스크립트 방법 과 특성은 기본값을 사용 할 수 있습니다.
Number Properties
숫자 속성
Property Description MAX_VALUE Returns the largest number possible in JavaScript MIN_VALUE Returns the smallest number possible in JavaScript NEGATIVE_INFINITY Represents negative infinity (returned on overflow) NaN Represents a "Not-a-Number" value POSITIVE_INFINITY Represents infinity (returned on overflow) MAX_VALUE 자바스크립트에서 가장 큰 수를 반환합니다. MIN_VALUE 자바스크립트에서 가장 작은 수를 반환합니다. NEGATIVE_INFINITY 음의 무한대(오버플로우 반환)를 반환합니다. NaN "Not-a-Number"값으로 대신합니다. POSITIVE_INFINITY 무한대(오버플로우 반환)를 반환합니다 Example var x = Number.MAX_VALUE;
Number properties belongs to the JavaScript’s number object wrapper called Number.
These properties can only be accessed as Number.MAX_VALUE.
Using myNumber.MAX_VALUE, where myNumber is a variable, expression, or value, will return undefined:
숫자 속성은 자바스크립트의 숫자 객체 래퍼에 속합니다.
이러한 속성은 전용으로 접근 할 수 있습니다. MAX_VALUE.
myNumber.MAX_VALUE, where myNumber is a variable, expression를 사용하면 값으로 undefined를 반환합니다.
Example var x = 6; var y = x.MAX_VALUE; // y becomes undefined
Number methods are covered in the next chapter
숫자 메소드에 대해서는 다음 장에서 설명 하겠습니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4]
JavaScript Number Methods
자바스크립트 숫자 메소드
Number methods help you to work with numbers.
숫자 메소드는 당신의 숫자를 동작하는데 도움이 될 것입니다.
Global Methods
전반적인 메소드
JavaScript global functions can be used on all JavaScript data types.
These are the most relevant methods, when working with numbers:
자바스크립트 전역 함수는 모든 자바스크립트 데이터 형식에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
숫자들을 적용할때에 가장 관련 있는 것들 입니다.
Method Description Number() Returns a number, converted from its argument. parseFloat() Parses its argument and returns a floating point number parseInt() Parses its argument and returns an integer Method Description Number() 인수의 숫자를 변환하여 반환합니다. parseFloat() 인수를 구문분석하고 부동소수점의 수를 반환합니다. parseInt() 인수를 구문분석하고 정수를 반환합니다.
Number Methods
숫자 메소드
JavaScript number methods are methods that can be used on numbers:
자바스크립트 숫자 메소드에서 숫자를 사용할 수 있는 방법 입니다.
Method Description toString() Returns a number as a string toExponential() Returns a string, with a number rounded and written using exponential notation. toFixed() Returns a string, with a number rounded and written with a specified number of decimals. toPrecision() Returns a string, with a number written with a specified length valueOf() Returns a number as a number Method Description toString() 숫자를 문자열로 반환합니다. toExponential() 지수법을 사용하여 반올림하여 문자열로 반환합니다. toFixed() 소수로 지정된 숫자를 반올림한 숫자를 문자열로 반환합니다. toPrecision() 지정된 길이로 작성된 숫자를 문자열로 반환합니다. valueOf() 숫자를 숫자로 반환해 줍니다.
All number methods return a new value. They do not change the original variable.
모든 숫자 메소드는 새로운 값을 반환합니다. 그들은 원래 변수를 변경하지 않습니다.
The toString() Method
toString() 메소드
toString() returns a number as a string.
All number methods can be used on any type of numbers (literals, variables, or expressions):
toString()은 숫자를 문자열로 반환합니다.
모든 숫자는 숫자 메소드(정수, 변수, 표현)중 어느 타입에서 사용될 수 있습니다.
Example var x = 123; x.toString(); // returns 123 from variable x (123).toString(); // returns 123 from literal 123 (100 + 23).toString(); // returns 123 from expression 100 + 23
The toExponential() Method
toExponential() 메소드
toExponential() returns a string, with a number rounded and written using exponential notation.
A parameter defines the number of characters behind the decimal point:
toExponential()에서는 반올림 지수 표기법을 사용하여 숫자를 문자열로 반환합니다.
파라미터는 소수점 뒤에 문자의 수를 정의합니다:
Example var x = 9.656; x.toExponential(2); // returns 9.66e+0 x.toExponential(4); // returns 9.6560e+0 x.toExponential(6); // returns 9.656000e+0
The parameter is optional. If you don’t specify it, JavaScript will not round the number.
인자값은 선택입니다. 당신이 그것을 지정하지 않을 경우에는 JavaScript는 반올림을 하지 않습니다.
The toFixed() Method
toFixed() 메소드
toFixed() returns a string, with the number written with a specified number of decimals:
toFixed()는 소수의 길이를 지정하고 길이만큼의 숫자를 문자열로 반환합니다.
Example var x = 9.656; x.toFixed(0); // returns 10 x.toFixed(2); // returns 9.66 x.toFixed(4); // returns 9.6560 x.toFixed(6); // returns 9.656000
toFixed(2) is perfect for working with money.
The toPrecision() Method
toPrecision() 메소드
toPrecision() returns a string, with a number written with a specified length:
toPrecision()은 지정된 길이로 작성된 숫자를 문자열로 반환합니다.
Example var x = 9.656; x.toPrecision(); // returns 9.656 x.toPrecision(2); // returns 9.7 x.toPrecision(4); // returns 9.656 x.toPrecision(6); // returns 9.65600
Converting Variables to Numbers
숫자 변수를 변환
There are 3 JavaScript functions that can be used to convert variables to numbers:
숫자를 변수로 변환하는데 사용될수 있는 함수로는 3가지가 있다
- The Number() method
- The parseInt() method
- The parseFloat() method
These methods are not number methods, but global JavaScript methods.
숫자 메소드 방법은 아니다, 하지만 전반적인 자바스크립트 방법이다.
The Number() Method
Number() 메소드
Number(), can be used to convert JavaScript variables to numbers:
Number()는 자바스크립트 변수를 숫자로 변환 할 수 있습니다.
Example x = true; Number(x); // returns 1 x = false; Number(x); // returns 0 x = new Date(); Number(x); // returns 1404568027739 x = "10" Number(x); // returns 10 x = "10 20" Number(x); // returns NaN
Used on Date(), the Number() method returns the number of milliseconds since 1.1.1970.
날짜와 숫자 메소드는 1970년 1월1일 이후의 밀리 초 수를 반환합니다.
The parseInt() Method
parseInt() 메소드
parseInt() parses a string and returns a whole number. Spaces are allowed. Only the first number is returned:
parseInt()는 문자열을 구문 분석하고 정수를 반환합니다. 공백을 허용합니다. 첫번째 숫자가 반환됩니다.
Example
parseInt("10"); // returns 10
parseInt("10.33"); // returns 10
parseInt("10 20 30"); // returns 10
parseInt("10 years"); // returns 10
parseInt("years 10"); // returns NaN
If the number cannot be converted, NaN (Not a Number) is returned.
수를 변환할 수 없을 경우에는 NaN(숫자가 아니다)를 반환합니다.
The parseFloat() Method
parseFloat() 메소드
parseFloat() parses a string and returns a number. Spaces are allowed. Only the first number is returned:
parseFloat()는 문자열을 구문 분석하고 수를 반환합니다. 공백이 허용됩니다. 첫번째 숫자가 반환됩니다.
Example
parseFloat("10"); // returns 10
parseFloat("10.33"); // returns 10.33
parseFloat("10 20 30"); // returns 10
parseFloat("10 years"); // returns 10
parseFloat("years 10"); // returns NaN
If the number cannot be converted, NaN (Not a Number) is returned.
수를 변환 할 수 없는 경우에는 NaN(숫자가 아니다)를 반환합니다.
The valueOf() Method
valueOf() 메소드
valueOf() returns a number as a number.
valueOf()은 숫자로 숫자를 반환합니다.
Example var x = 123; x.valueOf(); // returns 123 from variable x (123).valueOf(); // returns 123 from literal 123 (100 + 23).valueOf(); // returns 123 from expression 100 + 23
In JavaScript, a number can be a primitive value (typeof = number) or an object (typeof = object).
The valueOf() method is used internally in JavaScript to convert Number objects to primitive values.
There is no reason to use it in your code.
In JavaScript, all data types have a valueOf() and a toString() method.
자바스크립트에서 숫자는 원시값 또는 객체가 될 수 있습니다.
valueOf() 메서드는 기본값으로 번호 개체를 변환하는 자바스크립트에서 내부적으로 사용됩니다.
코드에서 그것을 사용하는 이유는
Complete JavaScript Number Reference
완벽한 자바스크립트 숫자 Reference
For a complete reference, go to our Complete JavaScript Number Reference.
The reference contains descriptions and examples of all Number properties and methods.
필요한 모든 것이 갖춰진 우리 자바스크립트 Number Reference참조. reference에는 모든 Number의 속성과 메소드에 대한 설명과 예제가 들어 있습니다.
JavaScript Math Object
자바스크립트 수학 객체
The Math object allows you to perform mathematical tasks on numbers.
Math 객체는 숫자에 수학적 작업을 수행 할 수 있습니다.
The Math Object
수학 객체
The Math object allows you to perform mathematical tasks.
The Math object includes several mathematical methods.
Math객체는 수학적 작업을 수행 할 수 있습니다.
Math객체의 목적은 여러가지 수학적인 방법을 포함하고 있습니다.
One common use of the Math object is to create a random number:
Math객체의 하나의 일반적인 사용방법은 임의의 숫자를 생성하는 것 입니다.
Example Math.random(); // returns a random number
Math has no constructor. No methods have to create a Math object first.
Math는 생성자가 없습니다. 수학 객체를 생성 할 필요는 없습니다.
Math.min() and Math.max()
Math.min() and Math.max() can be used to find the lowest or highest value in a list of arguments:
Math.min() 과 Math.max()는 인수 목록중에서 가장 낮거나 가장 높은 값을 찾기위해 사용됩니다.
Example Math.min(0, 150, 30, 20, -8, -200); // returns -200
Example Math.max(0, 150, 30, 20, -8, -200); // returns 150
Math.random()
Math.random() returns a random number between 0 (inclusive), and 1 (exclusive):
Math.random()은 0과 1사이에서 임의의 수를 반환합니다.
Example Math.random(); // returns a random number
Math.random() always returns a number lower than 1.
Math.random()은 항상 1보다 낮은 수를 반환합니다.
Math.round()
Math.round() rounds a number to the nearest integer:
Math.round()는 가장 가까운 정수로 숫자를 반올림 합니다.
Example Math.round(4.7); // returns 5 Math.round(4.4); // returns 4
Math.ceil()
Math.ceil() rounds a number up to the nearest integer:
Math.ceil()은 위쪽으로 가장 가까운 정수 입니다.
Example Math.ceil(4.4); // returns 5
Math.floor()
Math.floor() rounds a number down to the nearest integer:
Math.floor() 아래쪽으로 가장 가까운 정수 입니다.
Example Math.floor(4.7); // returns 4
Math.floor() and Math.random() can be used together to return a random number between 0 and 10:
Math.floor()과 Math.random()를 같이 사용하여 0부터 10 사이에 숫자를 랜덤으로 반환합니다.
Example Math.floor(Math.random() * 11); // returns a random number between 0 and 10
Math Constants
Math 정수
JavaScript provides 8 mathematical constants that can be accessed with the Math object:
자바스크립트는 수학 객체에 접근 할 수 있도록 8개의 수학적인 정수를 제공해 줍니다.
Example Math.E // returns Euler's number Math.PI // returns PI Math.SQRT2 // returns the square root of 2 Math.SQRT1_2 // returns the square root of 1/2 Math.LN2 // returns the natural logarithm of 2 Math.LN10 // returns the natural logarithm of 10 Math.LOG2E // returns base 2 logarithm of E Math.LOG10E // returns base 10 logarithm of E Math.E // 오일러의 수를 반환합니다. Math.PI // PI를 반환 합니다. Math.SQRT2 // 2의 제곱근을 반환 합니다. Math.SQRT1_2 // 1/2의 제곱근을 반환 합니다. Math.LN2 // 2의 자연 로그를 반환합니다. Math.LN10 // 10의 자연 로그를 반환합니다. Math.LOG2E // E의 기본 로그 반환 Math.LOG10E // E의10대수를 기반으로 반환
Math Object Methods
Math 오브젝트 메소드
Method Description abs(x) Returns the absolute value of x acos(x) Returns the arccosine of x, in radians asin(x) Returns the arcsine of x, in radians atan(x) Returns the arctangent of x as a numeric value between -PI/2 and PI/2 radians atan2(y,x) Returns the arctangent of the quotient of its arguments ceil(x) Returns x, rounded upwards to the nearest integer cos(x) Returns the cosine of x (x is in radians) exp(x) Returns the value of Ex floor(x) Returns x, rounded downwards to the nearest integer log(x) Returns the natural logarithm (base E) of x max(x,y,z,...,n) Returns the number with the highest value min(x,y,z,...,n) Returns the number with the lowest value pow(x,y) Returns the value of x to the power of y random() Returns a random number between 0 and 1 round(x) Rounds x to the nearest integer sin(x) Returns the sine of x (x is in radians) sqrt(x) Returns the square root of x tan(x) Returns the tangent of an angle abs(x) x의 절대 값을 반환합니다. acos(x) x의 라디안의 arccosine을 반환 합니다. asin(x) x의 라디안의 arcsine을 반환 합니다. atan(x) -PI/2와 PI/2 라디안 사이의 숫자 값으로 x의 arctangent를 반환 합니다. atan2(y,x) 인수의 몫의 arctangent를 반환합니다. ceil(x) 위쪽으로 가장 가까운정수를 반환합니다. cos(x) x의 코사인을 돌려줍니다. (x는 라디안) exp(x) E의 x승으로 값을 반환합니다. floor(x) 가장 가까운 정수로 아래로 반올림 합니다. log(x) x의 자연 로그를 돌려줍니다.(기본E) max(x,y,z,...,n) 가장 높은 값의 수를 돌려줍니다. min(x,y,z,...,n) 가장 낮은 값의 수를 돌려줍니다. pow(x,y) y의 동작에 x값을 반환합니다. random() 0과1 사이의 임의의 수를 반환합니다. round(x) 가장 가까운 정수를 반환합니다. sin(x) x의 사인을 반환 합니다. sqrt(x) x의 제곱근을 반환합니다. tan(x) 각에대한 탄젠트를 반환합니다.
Complete Math Reference
전체 수학 Reference
For a complete reference, go to our complete Math object reference.
The reference contains descriptions and examples of all Math properties and methods.
필요한 모든 것이 갖춰진 우리 자바스크립트 Math Reference참조. reference에는 모든 Math의 속성과 메소드에 대한 설명과 예제가 들어 있습니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4]
JavaScript Dates
자바스크립트 날짜
The Date object lets you work with dates (years, months, days, hours, minutes, seconds, and milliseconds)
Date객체는 (년, 월, 일, 시, 분, 초, 밀리초)를 처리 할 수 있습니다.
JavaScript Date Formats
자바스크립트 날짜 형식
A JavaScript date can be written as a string:
Mon Dec 21 2015 14:47:40 GMT+0900 (대한민국 표준시)
or as a number:
1450676860265
Dates written as numbers, specifies the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00.
자바스크립트 날짜는 문자열로 기록 될 수있습니다.
월 2015년 12월 21일 14시 47분 (그리니치 표준시)+ 0900(대한민국 표준시)
또는 숫자로:
1450676860265
숫자로 작성된 날짜는 1970년 1월 1일 00:00:00 이후로 밀리 초를 지정하였습니다.
Displaying Dates
날짜 표시
In this tutorial we use a script to display dates inside a <p> element with id=”demo”:
이 튜토리얼 안에서 우리는 id=”demo”dhk <p> 요소 배내에 날짜를 표시하는 스크립트 사용
Example
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = Date();
</script>
The script above says: assign the value of Date() to the content (innerHTML) of the element with id=”demo”.
위의 스크립트에서 말합니다: id=”demo”와 요소의내용(innerHTML을) 에 날짜 값()을 합니다
You will learn how to display a date, in a more readable format, at the bottom of this page.
이 페이지는 페이지 하단에 더 읽을 수 없는 형식으로, 날짜를 표시하는 방법을 배우울 것 입니다.
Creating Date Objects
날짜 객체 만들기
The Date object lets us work with dates.
A date consists of a year, a month, a day, an hour, a minute, a second, and milliseconds.
Date objects are created with the new Date() constructor.
There are 4 ways of initiating a date:
Date객체로 우리는 날짜 작업을 할 수 있습니다.
날짜는 년, 월, 일, 시, 분, 초, 밀리 초로 구성 되어 있습니다.
new Date()로 새로운 날짜 개체가 만들어 집니다.
날짜를 시작하는 4가지 방법이 있습니다.
new Date() new Date(milliseconds) new Date(dateString) new Date(year, month, day, hours, minutes, seconds, milliseconds)
Using new Date(), creates a new date object with the current date and time:
new Date()를 사용하면 Date객체를 새로만들어서 현재 날짜와 시간을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example
<script>
var d = new Date();
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = d;
</script>
Using new Date(date string), creates a new date object from the specified date and time:
문자열을 로 새로운 날짜를 사용하여 지정된 날짜 및 시간에서 새로운 Date객체를 만들수 있습니다.
Example
<script>
var d = new Date("October 13, 2014 11:13:00");
document.getElementById( "demo").innerHTML = d;
</script>
Valid date strings (date formats) are described in the next chapter.
Using new Date(number), creates a new date object as zero time plus the number.
Zero time is 01 January 1970 00:00:00 UTC. The number is specified in milliseconds:
유요한 날짜 문자열(날짜 형식)은 다음 장에 설명 되어 있습니다.
new Date(number)를 사용하더라도 0시간을 더한 번호로 새로운 날짜 개체를 만듭니다.
0시간은 1970년 1월 00:00시 수는 밀리터리 초로 표시합니다.
Example
<script>
var d = new Date(86400000);
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = d;
</script>
JavaScript dates are calculated in milliseconds from 01 January, 1970 00:00:00 Universal Time (UTC). One day contains 86,400,000 millisecond.
자바스크립트 날짜 1970년 1월 1일 00시 0분 0초 세계시(UTC)에서 밀리 초 단위로 계산됩니다.하루는 86,400,000밀리초를 포함합니다.
Using new Date(7 numbers), creates a new date object with the specified date and time:
The 7 numbers specify the year, month, day, hour, minute, second, and millisecond, in that order:
new Date(7 numbers)와 같이 새로운 date 객체를 생성하여 시간과 날짜를 설정할 수 있습니다.
7은 숫자 순서대로 년,월,일,시 ,분,초 를 지정합니다.
Example
<script>
var d = new Date(99,5,24,11,33,30,0);
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = d;
</script>
Variants of the example above let us omit any of the last 4 parameters:
예제는 우리는 4개의 파라미터 변수를 생략 할 수 있습니다.
Example
<script>
var d = new Date(99,5,24);
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = d;
</script>
JavaScript counts months from 0 to 11. January is 0. December is 11.
자바스크립트는 0부터 11개월 순서입니다. 1월은 0 이고 12월은 11입니다.
Date Methods
날짜 메소드
When a Date object is created, a number of methods allow you to operate on it.
Date methods allow you to get and set the year, month, day, hour, minute, second, and millisecond of objects, using either local time or UTC (universal, or GMT) time.
Date객체가 생성 될 때 다수의 방법은 당신이 그것을 동작할 수 있습니다.
date메소드는 시간을 현지 시간 또는 UTC를 사용하여 당신의 년 월 일 시 분을 얻어 고 두번째는 객체의 밀리초를 설정할 수 있도록 합니다.
Date methods are covered in a later chapter.
Date메소드는 뒷 장에서 설명합니다.
Displaying Dates
날짜 표시
When you display a date object in HTML, it is automatically converted to a string, with the toString() method.
당신이 date객체를 HTML에 표시할때 그것은 자동적으로 toString()메소드 처럼 문자열로 전환됩니다.
Example
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
d = new Date();
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = d;
</script>
Is the same as:
이것은 같을 수 있습니다.
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
d = new Date();
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = d.toString();
</script>
The toUTCString() method converts a date to a UTC string (a date display standard).
toUTCString()메소드는 UTC문자열(날짜 표시 기준)로 날짜를 변환합니다.
Example
<script>
var d = new Date();
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = d.toUTCString();
</script>
The toDateString() method converts a date to a more readable format:
toDateString() 메소드는 더 읽기 쉬운 구성으로 날짜를 변환합니다.
Example
<script>
var d = new Date();
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = d.toDateString();
</script>
Date objects are static, not dynamic. The computer time is ticking, but date objects, once created, are not.
Date객체는 동적, 정적이지 않습니다. 컴퓨터는 시간은 똑닥 거리지만 date 객체는 한번만들면 그렇지 않습니다.
Time Zones
시간대
When setting a date, without specifying the time zone, JavaScript will use the browser’s time zone.
When getting a date, without specifying the time zone, the result is converted to the browser’s time zone.
In other words: If a date/time is created in GMT (Greenwich Mean Time), the date/time will be converted to CDT (Central US Daylight Time) if a user browses from central US.
Read more about time zones in the next chapters.
시간대를 정하지 않고 날짜를 설정하면 자바스크립트는 브라우저의 시간대를 사용합니다.
날짜를 얻는 경우에는 시간대를 지정하지 않고 그 결과는 브라우저의 시간대로 변환됩니다.
날짜/ 시간은 GMT(그리니치 표준시)에 만든 경우 사용자가 중앙 미국에서 탐색 할 경우, 날짜 / 시간은 CDT(미국 중부 일광 절약 시간)로 변환됩니다.
다음 장에서 시간대에 대한 자세한 내용을 읽어 보시겠습니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
JavaScript Date Formats
자바스크립트 날짜 구성
JavaScript Date Input
자바스크립트 날짜 입력
There are generally 4 types of JavaScript date formats:
자바스크립트 날짜 구성에는 일반적으로 4가지 형태가 있습니다.
- ISO Dates
- Long Dates
- Short Dates
-
Full Format
- ISO 날짜
- 긴 날짜
- 짧은 날짜
- 전체 구성
JavaScript Date Output
자바스크립트 날짜 출력
Independent of input format, JavaScript will (by default) output dates in full text string format:
Wed Mar 25 2015 01:00:00 GMT+0100 (W. Europe Standard Time)
입력 형식의 독립을 위해서, 자바스크립트에는 전체 텍스트 문자열 형식으로 (기본적으로) 날짜를 출력하는 것입니다.
Wed Mar 25 2015 01:00:00 GMT+0100 (서부 유럽 시간기준)
JavaScript ISO Dates
자바스크립트 ISO날짜
ISO 8601 is the international standard for the representation of dates and times.
The ISO 8601 syntax (YYYY-MM-DD) is also the preferred JavaScript date format:
ISO8601은 날짜와 시간에 대한 국제적인 표준 입니다.
ISO8601문법은 (YYYY-MM-DD)이며 또한 자바스크립트에서 우선적으로 날짜 구성을 해야합니다.
Example (Complete date)
var d = new Date("2015-03-25");
It can be written without specifying the day (YYYY-MM):
그것은 일(YYYY-MM)을 사용하지 않고 쓰는것이 가능합니다.
Example (Year and month)
var d = new Date("2015-03");
It can be written without month and day (YYYY):
그것은 월과 일을 사용하지 않고 쓰는것이 가능합니다.
Example (Only year)
var d = new Date("2015");
It can be written with added hours, minutes, and seconds (YYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS):
그것은 시간, 분, 초를 추가하여 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example (Complete date plus hours, minutes, and seconds)
var d = new Date("2015-03-25T12:00:00");
The T in the date string, between the date and time, indicates UTC time.
UTC (Universal Time Coordinated) is the same as GMT (Greenwich Mean Time).
날짜문자열과 시간 사이에 T는 UTC시간을 나타냅니다.
UTC(세계 표준시)는 GMT(그리니치 표준시)와 같습니다.
JavaScript Long Dates.
자바스크립트 긴 날짜
Long dates are most often written with a “MMM DD YYYY” syntax like this:
긴 날짜는 자주 “MMM DD YYYY”와 비슷한 문법으로 쓰여집니다.
Example
var d = new Date("Mar 25 2015");
But, year, month, and day can be in any order:
하지만 년, 월, 일은 임의의 순서로도 가능합니다.
Example
var d = new Date("25 Mar 2015");
Example
var d = new Date("2015 Mar 25");
And, month can be written in full (January), or abbreviated (Jan):
그리고, 달은 1월(January)를 단축해서 1월(Jan)로 쓸 수도 있습니다.
Example
var d = new Date("January 25 2015");
Example
var d = new Date("Jan 25 2015");
Commas are ignored. Names are case insensitive:
콤마는 생략합니다. 이름은 대소문자를 구별하지 않습니다.
Example
var d = new Date("2015, JANUARY, 25");
JavaScript Short Dates.
자바스크립트 짧은 날짜
Short dates are most often written with an “MM/DD/YYYY” syntax like this:
짧은 날짜는 대부분 “MM/DD/YYYY”와 같은 문법으로 쓰여집니다.
Example
var d = new Date("03/25/2015");
Either “/” or “-“ can be used as a separator:
양쪽의 분리할 때는 / 또는 -를 사용합니다.
Example
var d = new Date("03-25-2015");
JavaScript will also accept “YYYY/MM/DD”:
게다가 자바스크립트는 “YYYY/MM/DD”를 받아들입니다.
Example
var d = new Date("2015/03/25");
Month is written before day in all short date and ISO date formats.
Full Date Format
전체 날짜 형식
JavaScript will accept date strings in “full JavaScript format”:
자바스크립트는 전체 자바스크립트 형식으로 날짜 문자열을 받아들입니다.
Example
var d = new Date("Wed Mar 25 2015 09:56:24 GMT+0100 (W. Europe Standard Time)");
JavaScript will ignore errors both in the day name and in the time parentheses:
자바스크립트는 날이름과 시간의 모든 오류를 무시합니다.
Example
var d = new Date("Fri Mar 25 2015 09:56:24 GMT+0100 (Tokyo Time)");
Time Zones
시간대
JavaScript accepts these time zones:
자바스크립트에는 이러한 시간대를 받아들입니다.
Time Zone Description UTC Coordinated Universal Time GMT Greenwich Mean Time EDT (US) Eastern Daylight Time CDT (US) Central Daylight Time MDT (US) Mountain Daylight Time PDT (US) Pacific Daylight Time EST (US) Eastern Standard Time CST (US) Central Standard Time MST (US) Mountain Standard Time PST (US) Pacific Standard Time
When setting a date, without specifying the time zone, JavaScript will use the browser’s time zone.
When getting a date, without specifying the time zone, the result is converted to the browser’s time zone.
In other words: If a date/time is created in GMT (Greenwich Mean Time), the date/time will be converted to CDT (Central US Daylight Time) if a user browses from central US.
시간대를 설정하지 않고 날짜를 사용하면 자바스크립트는 브라우저의 시간대를 사용합니다.
날짜를 가져올때 시간대를 정하지않으면 그 결과는 브라우저의 시간대로 변환됩니다.
다시말해서: 날짜/시간은 GMT에 만든경우 사용자가 중앙 미국에서 탐색할 경우 날짜 시간은 CDT로 변환됩니다.
JavaScript Arrays
자바스크립트 배열
JavaScript arrays are used to store multiple values in a single variable.
자바스크립트 배열은 하나의 변수에 여러가지 값들을 저장하는데 사용합니다.
Displaying Arrays
배열 표시
In this tutorial we will use a script to display arrays inside a <p> element with id=”demo”:
이 튜토리얼에서 우리는 스크립트를 <p> 요소의 id=”demo”안에서 배열을 보여주기 위해 사용하였습니다.
Example
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
var cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = cars;
</script>
The first line (in the script) creates an array named cars.
The second line “finds” the element with id=”demo”, and “displays” the array in the “innerHTML” of it.
첫번째 (스크립트에서)줄에 이름이 cars인 배열을 생성 하였습니다.
두번째 줄에서 요소의 id=”demo”인 것을 찾고 innerHTML로 배열을 보여줍니다.
Try it Yourself
혼자 해보기
Create an array, and assign values to it:
배열을 만들고 그것의 안에다가 값들을 넣는다
Example var cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"];
Spaces and line breaks are not important. A declaration can span multiple lines:
줄 바꿈과 띄워쓰기는 중요하지 않습니다. 여러줄에 선언할 수 있습니다.
Example
var cars = [
"Saab",
"Volvo",
"BMW"
];
Never put a comma after the last element (like “BMW”,). The effect is inconsistent across browsers.
절대 마지막 요소 다음에는 콤마를 찍지 말아야 합니다. 그것은 브라우저에서 다른 결과를 나오게 합니다.
What is an Array?
배열이란 무엇인가?
An array is a special variable, which can hold more than one value at a time.
If you have a list of items (a list of car names, for example), storing the cars in single variables could look like this:
배열은 한번에 여러개의 값들을 갖을 수 있는 특별한 변수 입니다.
만약 당신이 가지고 있는 목록(예를들면 차 이름), 차 하나의 변수에 보이는 것과 비슷한 것들을 저장할 수 있습니다.
var car1 = "Saab"; var car2 = "Volvo"; var car3 = "BMW";
However, what if you want to loop through the cars and find a specific one? And what if you had not 3 cars, but 300?
The solution is an array!
An array can hold many values under a single name, and you can access the values by referring to an index number.
그러나 당신이 원하는 정보를 얻으려고 하는 경우에 3개의 차가 아닌 300개라면?
해결 책은 배열입니다!
배열은 하나로 여러개의 값을 받아들일 수 있으며 인덱스 번호를 참조하여 접근 할 수 있습니다.
Creating an Array
배열 생성
Using an array literal is the easiest way to create a JavaScript Array.
배열 리터럴을 사용하여 자바스크립트 배열을 생성할 수 있는 가장 쉬운방법 입니다.
Syntax: var array-name = [item1, item2, ...]; Example: var cars = ["Saab", "Volvo", "BMW"];
Using the JavaScript Keyword new
자바스크립트 새로운 키워드 사용
The following example also creates an Array, and assigns values to it:
다음 예제는 배열을 생성하고 값을 할당하는 예제 입니다.
Example
var cars = new Array("Saab", "Volvo", "BMW");
The two examples above do exactly the same. There is no need to use new Array().
For simplicity, readability and execution speed, use the first one (the array literal method).
위에의 2개 정확하게 같은 예제 입니다. 거기에는 new Array()를 사용할 필요가 없습니다.
단순성, 가독성과 실행 속도의 경우에는 첫번째를 사용 합니다.
Access the Elements of an Array
배열의 요소에 접근
You refer to an array element by referring to the index number.
This statement accesses the value of the first element in cars:
당신은 배열의 요소에대한 index number를 참고하여 참조하십시오.
이것은 차 요소의 첫번째 값에 대한 접근 방법을 설명한 것 입니다.
var name = cars[0];
This statement modifies the first element in cars:
이것은 차 요소의 첫번째를 수정하는 방법을 설명한 것 입니다.
cars[0] = “Opel”;
[0] is the first element in an array. [1] is the second. Array indexes start with 0.
[0]은 배열의 첫번째 요소 입니다. [1]은 2번째 입니다. 배열 인덱스의 시작은 0부터 입니다.
You Can Have Different Objects in One Array
당신의 배열과 오브젝트는 차이점을 가지고 있습니다.
JavaScript variables can be objects. Arrays are special kinds of objects.
Because of this, you can have variables of different types in the same Array.
You can have objects in an Array. You can have functions in an Array. You can have arrays in an Array:
자바스크립트 변수는 오브젝트로 가능합니다. 배열은 특별한 오브젝트 종류 입니다.
때문에 같은 배열에서 서로 다른 형태의 변수를 가질 수 있습니다.
당신은 배열 안에 오브젝트를 가질 수 있습니다. 당신은 배열에 함수를 가질 수 있습니다. 당신은 배열에 배열들을 가질 수 있습니다.
myArray[0] = Date.now; myArray[1] = myFunction; myArray[2] = myCars;
Arrays are Objects
배열의 오브젝트
Arrays are a special type of objects. The typeof operator in JavaScript returns “object” for arrays.
But, JavaScript arrays are best described as arrays.
Arrays use numbers to access its “elements”. In this example, person[0] returns John:
배열은 특별한 형식의 오브젝트 입니다. 자바스크립트에서 배열은 typeof연산자로 “오브젝트”를 반환합니다.
하지만 배열은 가장좋은 배열로 설명 되어 있습니다.
배열에서는 요소에 숫자로 접근할 수 있습니다. 예를들면 person[0]은 John을 반환합니다.
Array: var person = ["John", "Doe", 46];
Objects use names to access its “members”. In this example, person.firstName returns John:
오브젝트는 접근할때 해당 이름을 사용하여 접근 합니다. 이 예제는, person.firstName은 John을 반환합니다.
Object:
var person = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe", age:46};
Array Properties and Methods
배열의 속성과 방법
The real strength of JavaScript arrays are the built-in array properties and methods:
자바스크립트 배열의 진정한 힘은 내장된 배열의 속성과 메소드 입니다.
Examples var x = cars.length; // The length property returns the number of elements in cars var y = cars.sort(); // The sort() method sort cars in alphabetical order
Array methods are covered in the next chapter.
배열 방법에 대해서는 다음잘에서 배울 것입니다
The length Property
길이 속성
The length property of an array returns the length of an array (the number of array elements).
배열에서의 길이 속성은 배열의 길이를 반환합니다.(배열 요소의 갯수)
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.length; // the length of fruits is 4
The length property is always one more than the highest array index.
길이 속성은 배열에서 가장높은 인덱스에 1을 더합니다.
Adding Array Elements
배열 요소 추가하기
The easiest way to add a new element to an array is using the push method:
새로운 요소를 배열에 추가하는 가장쉬운 방법은 push메소도를 사용해서 추가하는 방법입니다.
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.push("Lemon"); // adds a new element (Lemon) to fruits
New element can also be added to an array using the length property:
또한 새로운 요소는 길이 속성을 사용해서 배열에 추가할 수 있습니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits[fruits.length] = "Lemon"; // adds a new element (Lemon) to fruits
Adding elements with high indexes can create undefined “holes” in an array:
배열은 높은 인덱스르르 사용해서 빈 배열을 만들 수도 있습니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits[10] = "Lemon"; // adds a new element (Lemon) to fruits
Looping Array Elements
배열 요소 루프
The best way to loop through an array, is using a “for” loop:
배열에 루프문을 사용하는 방법중 가장 좋은 방법은 입니다
Example
var index;
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
for (index = 0; index < fruits.length; index++) {
text += fruits[index];
}
Associative Arrays
연관된 배열
Many programming languages support arrays with named indexes.
Arrays with named indexes are called associative arrays (or hashes).
JavaScript does not support arrays with named indexes.
In JavaScript, arrays always use numbered indexes.
많은 프로그래밍 언어는 익덱스 배열을 지원합니다.
인덱스 배열은 연관배열(또는 해시)라고 합니다.
자바스크립트 배열은 이름에 인덱스 배열을 지원합니다.
자바스크립트 배열은 항상 인덱스 번호를 사용합니다.
Example var person = []; person[0] = "John"; person[1] = "Doe"; person[2] = 46; var x = person.length; // person.length will return 3 var y = person[0]; // person[0] will return "John"
WARNING !! If you use a named index, JavaScript will redefine the array to a standard object. After that, all array methods and properties will produce incorrect results.
경고!!
만약 당신이 인덱스 이름을 사용하면 자바스크립트 표준객체를 재정의 합니다.
그 후 모든 배열 메서드와 속성이 잘못된 결과를 생성합니다.
Example: var person = []; person["firstName"] = "John"; person["lastName"] = "Doe"; person["age"] = 46; var x = person.length; // person.length will return 0 var y = person[0]; // person[0] will return undefined
The Difference Between Arrays and Objects
배열과 객체 사이에서의 차이점
In JavaScript, arrays use numbered indexes.
In JavaScript, objects use named indexes.
Arrays are a special kind of objects, with numbered indexes.
자바스크립트에서는 배열은 인덱스로 숫자를 사용합니다.
자바스크립트에서는 객체는 인덱스로 이름을 사용합니다.
배열은 인덱스로 숫자를 사용하는 객체의 종류 중 하나입니다.
When to Use Arrays. When to use Objects.
배열과 오브젝트를 사용하는 경우
- JavaScript does not support associative arrays.
- You should use objects when you want the element names to be strings (text).
-
You should use arrays when you want the element names to be numbers.
- 자바스크립트는 연관배열을 지원하지 않습니다.
- 문자 요소의 이름으로 문자열을 원한다면 당신은 객체를 사용 해야합니다.
- 요소 이름에 숫자를 원한다면 당신은 배열을 사용해야 합니다.
Avoid new Array()
new Array()의 다른방법
There is no need to use the JavaScript’s built-in array constructor new Array().
Use [] instead.
These two different statements both create a new empty array named points:
자바스크립트의 내장 배열 생성자를 사용할 필요가 없습니다.
대신에 []를 사용합니다.
이 두개의 서로다른 문은 모두 빈 배열을 만듭니다.
var points = new Array(); // Bad var points = []; // Good
These two different statements both create a new array containing 6 numbers:
이 두개의 서로다른 문은 모두 6이라는 숫자를 포함하는 새로운 배열을 만드는 것 입니다.
var points = new Array(40, 100, 1, 5, 25, 10) // Bad var points = [40, 100, 1, 5, 25, 10]; // Good
The new keyword only complicates the code. It can also produce some unexpected results:
새로운 키워드는 코드를 복잡하게 합니다. 또한 예상 밖의 결과가 발생할 수 있습니다.
var points = new Array(40, 100); // Creates an array with two elements (40 and 100)
What if I remove one of the elements?
만약 내가 하나의 요소를 제거한다면?
var points = new Array(40); // Creates an array with 40 undefined elements !!!!!
How to Recognize an Array
배열을 인식하는 요령
A common question is: How do I know if a variable is an array?
The problem is that the JavaScript operator typeof returns “object”:
일반적인 질문 : 변수가 배열인 경우 어떻게 알 수 있을까?
문제는 자바스크립트 연산자인 typeof는 개체를 반환합니다.
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; typeof fruits; // returns object
The typeof operator returns object because a JavaScript array is an object.
Solution 1:
To solve this problem ECMAScript 5 defines a new method Array.isArray():
자바스크립트 배열은 객체이기 때문에 typeof 연산자의 값이 Object입니다.
해결방법 1:
ECMAScript 5 는 새로운 방법 Array.isArray 를 정의 하고 이 문제를 해결하려면
Array.isArray(fruits); // returns true
The problem with this solution is that ECMAScript 5 is not supported in older browsers.
Solution 2:
To solve this problem you can create your own isArray() function:
이 솔루션의 문제는 ECMAScript 5에서 된다는 것 입니다 이전버전의 브라우저 에서는 지원하지 않습니다.
해결방법 2:
당신은 하나의 isArray()함수를 생성해서 이 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
function isArray(x) {
return x.constructor.toString().indexOf("Array") > -1;
}
The function above always returns true if the argument is an array.
Or more precisely: it returns true if the object prototype contains the word “Array”.
Solution 3:
The instanceof operator returns true if an object is created by a given constructor:
인수가배열인 경우 항상 위의 함수는 true를 반환합니다.
또는 더 정확하게: 객체의 트로토 타입이 배열을 포함하는 경우에는 true를 반환합니다.
해결방법 3:
instanceof 객체가 주어진 생성자에 의해 생성되는 경우에 연산자는 true를 반환합니다.
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits instanceof Array // returns true
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
JavaScript Array Methods
자바스크립트 Array Methods
The strength of JavaScript arrays lies in the array methods.
자바스크립트 배열의 장점은 arrays methods에 있습니다.
Converting Arrays to Strings
문자열을 배열로 전환
The JavaScript method toString() converts an array to a string of (comma separated) array values.
자바스크립트 toString()메소드는 배열값을 문자열로 변환을 시켜줍니다.(쉼표로 분리)
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = fruits.toString();
Result
Banana,Orange,Apple,Mango
The join() method also joins all array elements into a string.
It behaves just like toString(), but in addition you can specify the separator:
join()메소드 또한 모든 배열의 요소를 문자열로 연결시켜 줍니다.
toString()과 비슷하게 실행은 되지만, 당신이 분리할 기호를 추가할 수 있습니다.
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange","Apple", "Mango"];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = fruits.join(" * ");
Result
Banana * Orange * Apple * Mango
Popping and Pushing
빼고 넣습니다.
When you work with arrays, it is easy to remove elements and add new elements.
This is what popping and pushing is:
Popping items out of an array, or pushing items into an array.
배열로 작업을 할때, 그것은 쉽게 요소를 제거하거나 새로운 요소를 추가할 수 있습니다.
그것은 빼내하거나 넣을 수 있습니다.
popping은 배열에서 항목을 빼내고, 또는 puching은 배열에 항목을 추가합니다.
Popping
빼기
The pop() method removes the last element from an array:
pop()메소드는 배열에서 마지막 요소를 제거합니다.
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.pop(); // Removes the last element ("Mango") from fruits
The pop() method returns the value that was “popped out”:
pop()메서드는 빼내어 제거된 값을 반환합니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; var x = fruits.pop(); // the value of x is "Mango"
Pushing
밀어넣기
The push() method adds a new element to an array (at the end):
pushh()메소드는 배열(끝부분)의 새로운 요소를 추가시켜 줍니다.
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.push("Kiwi"); // Adds a new element ("Kiwi") to fruits
The push() method returns the new array length:
push()메소드는 새로운 배열의 길이를 반환합니다.
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
var x = fruits.push("Kiwi"); // the value of x is 5
Shifting Elements
엘리먼트 이동
Shifting is equivalent to popping, working on the first element instead of the last.
The shift() method removes the first element of an array, and “shifts” all other elements one place up.
Shifting은 첫번째 요소를 튕겨내는 일을 대신해서 합니다.
shift()메소드는 배열의 첫번째 요소를 제거하고, 모든 다른 요소들을 하나씩 위치를 올립니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.shift(); // Removes the first element "Banana" from fruits
The unshift() method adds a new element to an array (at the beginning), and “unshifts” older elements:
unshift() 메소드는 새로운 배열의 시작에 새로운 요소를 추가하고, 이전의 요소를 되돌려 줍니다.
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.unshift("Lemon"); // Adds a new element "Lemon" to fruits
The shift() method returns the string that was “shifted out”.
The unshift() method returns the new array length.
shift() 메소드는 옮겨지는 문자열을 반환합니다.
unshift() 메소드는 새로울 배열의 길이를 반환합니다.
Changing Elements
요소 변경
Array elements are accessed using their index number:
Array indexes start with 0. [0] is the first array element, [1] is the second, [2] is the third ….
배열요소들은 인덱스 번호를 사용하여 연결합니다.
배열의 인덱스들은 0부터 시작합니다. [0]은 첫번째 배열의 요소 [1]두번째 [3] 세번째…
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits[0] = "Kiwi"; // Changes the first element of fruits to "Kiwi"
The length property provides an easy way to append a new element to an array:
길이 속성은 배열에 새로운 요소를 쉽게 추가할 수 있도록 공급해 줍니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits[fruits.length] = "Kiwi"; // Appends "Kiwi" to fruit
Deleting Elements
삭제 요소
Since JavaScript arrays are objects, elements can be deleted by using the JavaScript operator delete:
자바스크립트는 배열 객체 입니다. 자바스크립트 연산자 삭제를 사용하여 요소를 제거할 수 있습니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; delete fruits[0]; // Changes the first element in fruits to undefined
Using delete on array elements leaves undefined holes in the array. Use pop() or shift() instead.
delete를 사용하여 배열의 요소를 정의되지않는 구멍을 만들어 냅니다. 대신에 pop()이나 shift()를 사용합니다.
Splicing an Array
배열 짜맞추기
The splice() method can be used to add new items to an array:
splice()메소드는 배열에 새 항목을 추가할 수 있습니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.splice(2, 0, "Lemon", "Kiwi");
The first parameter (2) defines the position where new elements should be added (spliced in).
The second parameter (0) defines how many elements should be removed.
The rest of the parameters (“Lemon” , “Kiwi”) define the new elements to be added.
첫번째 parameter(2)는 새로운 요소가 추가되어야 하는 위치를 정의합니다.
두번째 parameter(0)는 몇개의 요소를 재거할 건지를 결정 합니다.
parameter의 나머지는 새로 추가될 요소들을 정의합니다.
Using splice() to Remove Elements
요소를 제어하는 splice()사용
With clever parameter setting, you can use splice() to remove elements without leaving “holes” in the array:
parameter설정을 하면 배열에 구멍을 내지 않고 요소를 제거하기 위해서 splice()를 사용합니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.splice(0, 1); // Removes the first element of fruits
The first parameter (0) defines the position where new elements should be added (spliced in).
The second parameter (1) defines how many elements should be removed.
The rest of the parameters are omitted. No new elements will be added.
첫번째 parameter(0)은 새로운 요소가 추가되어야 하는 위치를 정의합니다.
두번째 parameter(1)는 얼마나 많은 요소가 제거 되어야 하는지를 정의합니다.
parameter의 나머지는 생략 됩니다. 새로운 요소가 추가되지 않습니다.
Sorting an Array
배열 정렬
The sort() method sorts an array alphabetically:
sort() 메소드는 알파벳 순으로 배열을 정렬시킵니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.sort(); // Sorts the elements of fruits
Reversing an Array
배열 역순
The reverse() method reverses the elements in an array.
You can use it to sort an array in descending order:
reverse() 메소드는 배열의 요소를 역순으로 정렬합니다.
당신은 내림차순으로 배열을 정렬하는데 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"]; fruits.sort(); // Sorts the elements of fruits fruits.reverse(); // Reverses the order of the elements
Numeric Sort
숫자 정렬
By default, the sort() function sorts values as strings.
This works well for strings (“Apple” comes before “Banana”).
However, if numbers are sorted as strings, “25” is bigger than “100”, because “2” is bigger than “1”.
Because of this, the sort() method will produce incorrect result when sorting numbers.
You can fix this by providing a compare function:
기본적으로, sort()함수는 문자열 값을 정렬합니다.
이 문자열은 정상적으로 작동합니다.(사과와 바나나 앞에)
번호가 문자열로 되어 있는 경우에는 2보다 1이 크기 때문에 100보다 25가 큽니다.
그렇기 때문에 숫자를 정렬할 때는 sort()메소드는 잘못된 결과를 생성합니다.
당신은 비교 기능으로 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
Example
var points = [40, 100, 1, 5, 25, 10];
points.sort(function(a, b){return a-b});
or
Example
var points = [40, 100, 1, 5, 25, 10];
points.sort(function(a, b){return a>b});
Use the same trick to sort an array descending:
배열 내림차순으로 트릭으로 정렬 같이 사용할 수 있습니다.
Example
var points = [40, 100, 1, 5, 25, 10];
points.sort(function(a, b){return b-a});
or
Example
var points = [40, 100, 1, 5, 25, 10];
points.sort(function(a, b){return b>a});
The Compare Function
비교 함수
The purpose of the compare function is to define an alternative sort order.
The compare function should return a negative, zero, or positive value, depending on the arguments:
비교 함수의 목적은 정렬 순서를 정의 하는 것 입니다.
비교 함수는 인수에 따라 +,-,0의 값을 반환해야 합니다.
function(a, b){return a-b}
When the sort() function compares two values, it sends the values to the compare function, and sorts the values according to the returned (negative, zero, positive) value.
sort() 함수는 두 값을 비교하여 함수 값을 전송하고 음,양,0 의 값에 따라 값들을 정렬 합니다.
Example:
When comparing 40 and 100, the sort() method calls the compare function(40,100).
The function calculates 40-100, and returns -60 (a negative value).
The sort function will sort 40 as a value lower than 100.
예:
40과 100을 sort() 메소드로 비교하려면 function(40,100)로 비교함수를 호출합니다.
함수에서 40-100은 -60을 반환합니다.(음의 값)
정렬 기능은 100보다 낮은 값으로 40을 정렬합니다.
Find the Highest (or Lowest) Value
최고갑 최저값 찾기
How to find the highest value in an array?
어떻게 배열에서 가장 높은 값을 찾을까요?
Example
var points = [40, 100, 1, 5, 25, 10];
points.sort(function(a, b){return b-a});
// now points[0] contains the highest value
And the lowest:
그리고 최저는:
Example
var points = [40, 100, 1, 5, 25, 10];
points.sort(function(a, b){return a-b});
// now points[0] contains the lowest value
Joining Arrays
배열 연결
The concat() method creates a new array by concatenating two arrays:
concat() 메소드는 두개의 배열을 하나로 연결하여 새로운 배열로 만들어 냅니다.
Example var myGirls = ["Cecilie", "Lone"]; var myBoys = ["Emil", "Tobias","Linus"]; var myChildren = myGirls.concat(myBoys); // Concatenates (joins) myGirls and myBoys
The concat() method can take any number of array arguments:
concat()메소드는 배열 인수를 무제한으로 수행 할 수 있습니다.
Example var arr1 = ["Cecilie", "Lone"]; var arr2 = ["Emil", "Tobias","Linus"]; var arr3 = ["Robin", "Morgan"]; var myChildren = arr1.concat(arr2, arr3); // Concatenates arr1 with arr2 and arr3
Slicing an Array
배열 조각
The slice() method slices out a piece of an array into a new array.
This example slices out a part of an array starting from array element 1 (“Orange”):
slice()메소드는 배열의 조각을 새로운 배열이 됩니다.
예제는 배열의 요소1부터 시작하는 조각낸 배열 입니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Lemon", "Apple", "Mango"]; var citrus = fruits.slice(1);
Array indexes start with 0. [0] is the first array element, [1] is the second, [2] is the third ….
This example slices out a part of an array starting from array element 3 (“Apple”):
배열 인덱스는 [0]첫번째 배열요소 [1] 두번째, [2]세번째…
이 예제는 배열 요소3부터 배열의 일부분을 조각낸 배열 입니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Lemon", "Apple", "Mango"]; var citrus = fruits.slice(3);
The slice() method can take two arguments like slice(1,3).
The method then selects elements from the start argument, and up to (but not including) the end argument.
slice()메소드는 slice(1,3)과 같이 2개의 인수로 할 수 있습니다.
이 메소드는 종료요소를 시작 요소로 선택하고 끝나는 요소도 선택 합니다.(하지만 끝지점 요소는 포함하지 않습니다.)
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Lemon", "Apple", "Mango"]; var citrus = fruits.slice(1, 3);
If the end argument is omitted, like in the first examples, the slice() method slices out the rest of the array.
만약 끝나는 인수가 첫번째 실수 예에서와 같이 생략 되면 slice()메소드는 나머지 조각을 빼냅니다.
Example var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Lemon", "Apple", "Mango"]; var citrus = fruits.slice(2);
The valueOf() Method
valueOf() 메소드
The valueOf() method is the default behavior for an array. It converts an array to a primitive value.
JavaScript will automatically convert an array to a string when a primitive value is expected.
Because of this, all these examples will produce the same result:
valueOf()메소드는 배열의 기본 동작입니다. 그것은 기본 값으로 배열을 반환합니다.
원시 값이 예상되는 경우 자바 스크립트가 자동으로 문자열로 배열을 변환합니다.
때문에 모든 이러한 예는 동일한 결과를 생성합니다.
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = fruits;
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = fruits.valueOf();
Example
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = fruits.toString();
All JavaScript objects have the valueOf() and toString() methods.
모든 자바스크립트는 객체는 valueOf() 및 toString()메서드가 있습니다.
Complete Array Reference
전체 배열 Rederence
For a complete reference, go to our Complete JavaScript Array Reference.
The reference contains descriptions and examples of all Array properties and methods.
필요한 모든 것이 갖춰진 우리 자바스크립트 Array Reference참조.
reference에는 모든 Array의 속성과 메소드에 대한 설명과 예제가 들어 있습니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5]
JavaScript Booleans
자바스크립트 Booleans
A JavaScript Boolean represents one of two values: true or false.
자바스크립트 boolean은 참 또는 거짓 2개중에 하나를 나타냅니다.
Boolean Values
Boolean값
Very often, in programming, you will need a data type that can only have one of two values, like
- YES / NO
- ON / OFF
- TRUE / FALSE
For this, JavaScript has a Boolean data type. It can only take the values true or false.
당신은 프로그래밍을 하면서 매우 자주 데이터 형식에 2개중 하나의 비슷한 값들을 필요로 할 것 입니다.
- YES / NO
- ON / OFF
- TRUE / FALSE
그것을 하기위해 자바스크립트 Boolean데이터 형식이 필요합니다. 이것은 오직 참과 거깃 값만 가지고 있습니다.
The Boolean() Function
Boolean() 함수
You can use the Boolean() function to find out if an expression (or a variable) is true:
당신은 Boolean() 함수에서 true 값을 밖으로 표현하여 사용하는 것이 가능합니다.
Example Boolean(10 > 9) // returns true Or even easier: 더 쉽게는: Example (10 > 9) // also returns true 10 > 9 // also returns true
Comparisons and Conditions
비교와 조건
The chapter JS Comparisons gives a full overview of comparison operators.
The chapter JS Conditions gives a full overview of conditional statements.
Here are some examples:
JS장에서 비교는 비교 연산자의 전체 개요에 대해서 제공해 줍니다.
JS장에서 조건은 조건부에 대하여 전체 개요를 제공해 줍니다.
예를들면 다음과 같습니다:
Operator Description Example == equal to if (day == "Monday") > greater than if (salary > 9000) < less than if (age < 18)
The Boolean value of an expression is the fundament for JavaScript comparisons and conditions.
Boolean값 표현은 자바스크립트의 기초가 되는 비교와 조건 입니다.
Everything With a “Real” Value is True
모든 값이 True인 실제 값들
Examples 100 3.14 -15 "Hello" "false" 7 + 1 + 3.14 5 < 6
Everything Without a “Real” is False
모든 값이 False인 실제 값들
The Boolean value of 0 (zero) is false: Boolean값이 0이면 false: var x = 0; Boolean(x); // returns false The Boolean value of -0 (minus zero) is false: Boolean값이 -0 이면 false: var x = -0; Boolean(x); // returns false The Boolean value of "" (empty string) is false: Boolean값이 "" 공백 문자열 이면 false: var x = ""; Boolean(x); // returns false The Boolean value of undefined is false: Boolean값이 존재 하지 않으면 false: var x; Boolean(x); // returns false The Boolean value of null is false: Boolean값이 null이면 false: var x = null; Boolean(x); // returns false The Boolean value of false is (you guessed it) false: Boolean값이 false이면 false: var x = false; Boolean(x); // returns false The Boolean value of NaN is false: Boolean값이 숫자가 아닌값이면 false var x = 10 / "H"; Boolean(x); // returns false
Boolean Properties and Methods
Boolean의 성질과 방법
Primitive values, like true and false, cannot have properties or methods (because they are not objects).
But with JavaScript, methods and properties are also available to primitive values, because JavaScript treats primitive values as objects when executing methods and properties.
참과 거짓과 같은 원시 값은 속성이나 메소드를 가질 수 없습니다.(때문에 그들은 객체가 아닙니다.)
메소드와 속성을 실행할 때 자바스크립트 객체로 원시값을 처리하기 때문에 자바스크립트 메소드 및 특성은 원시 값을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Complete Boolean Reference
필요한 모든 것이 갖춰진 Boolean Reference
For a complete reference, go to our Complete JavaScript Boolean Reference.
The reference contains descriptions and examples of all Boolean properties and methods.
필요한 모든 것이 갖춰진 우리 자바스크립트 Boolean reference 참조
reference에는 모든 Boolean의 속성과 메소드에 대한 설명과 예제가 들어 있습니다.
JavaScript Comparison and Logical Operators
자바스크립트 비교와 논리 연산자
Comparison and Logical operators are used to test for true or false.
비교와 논리 연산자는 참 또는 거짓을 테스트 할 때 사용합니다.
Comparison Operators
비교 연산자
Comparison operators are used in logical statements to determine equality or difference between variables or values.
Given that x = 5, the table below explains the comparison operators:
비교 연산자는 변수 나 값 사이에 동등하거나 차이를 결정하는 논리적인 문장에 사용됩니다.
x가 5로 정해진, 아래표에 비교 연산자에 대해서 설명 되어 있습니다.
Operator Description Comparing Returns == equal to x == 8 false x == 5 true x == "5" true ----------------------------------------------------------------------- === equal value and equal type x === 5 true x === "5" false ----------------------------------------------------------------------- != not equal x != 8 true ----------------------------------------------------------------------- !== not equal value or not equal type x !== 5 false x !== "5" true x !== 8 true ----------------------------------------------------------------------- > greater than x > 8 false ----------------------------------------------------------------------- < less than x < 8 true ----------------------------------------------------------------------- >= greater than or equal to x >= 8 false ----------------------------------------------------------------------- <= less than or equal to x <= 8 true
How Can it be Used
어떻게 사용이 가능한가
Comparison operators can be used in conditional statements to compare values and take action depending on the result:
비교 연산자는 조건문에서 값을 비교하거나 이동에 따라 다음 결과처럼 사용할 수 있습니다.
if (age < 18) text = "Too young";
You will learn more about the use of conditional statements in the next chapter of this tutorial.
당신은 조건문에 대한 사용 방법에 대해서 이 튜토리얼의 다음장에서 배우게 될 것입니다.
Logical Operators
논리 연산자
Logical operators are used to determine the logic between variables or values.
Given that x = 6 and y = 3, the table below explains the logical operators:
논리연산자는 변수 또는 값 사이에 논리적으로 결정하는데 사용됩니다.
x에6을 y에3을 대입합니다, 아래의 표는 논리연산자에 대한 설명입니다.
Operator Description Example && and (x < 10 && y > 1) is true || or (x == 5 || y == 5) is false ! not !(x == y) is true
Conditional (Ternary) Operator
조건(삼항) 연산자
JavaScript also contains a conditional operator that assigns a value to a variable based on some condition.
자바스크립트는 일부 조건에 따라 변수에 값을 할당하는 조건 연산자가 포함되어 있습니다.
Syntax
문법
variablename = (condition) ? value1:value2 Example var voteable = (age < 18) ? "Too young":"Old enough";
If the variable age is a value below 18, the value of the variable voteable will be “Too young”, otherwise the value of voteable will be “Old enough”.
만약 나이변수가 18보다 아래인 값이면, 변수voteable의 값은 “Too young”일 것이고, 아니면 voteable의 값은 “Old enough”일 것입니다.
Comparing Different Types
다른 형식 비교
Comparing data of different types may give unexpected results.
When comparing a string with a number, JavaScript will convert the string to a number when doing the comparison. An empty string converts to 0. A non-numeric string converts to NaN which is always false.
다른 유형의 데이터를 비교하면 예상치 못한 결과값을 가질 수 있습니다.
문자열과 숫자를 비교할 때 자바스크립트 문자열을 숫자로 변환합니다. 0이 아닌 숫자 문자열로 변환되고 빈 문자열은 항상 false인 NaN으로 변환 합니다.
Case Value 2 < 12 true 2 < "12" true 2 < "John" false 2 > "John" false 2 == "John" false "2" < "12" false "2" > "12" true "2" == "12" false
When comparing two strings, “2” will be greater than “12”, because (alphabetically) 1 is less than 2.
To secure a proper result, variables should be converted to the proper type before comparison:
두 문자열을 비교할 때는 (알파벳 순으로)1이 2보다 작기 때문에 “2”가 “12”보다 큽니다.
안전하고 적절한 결과를 얻기 위해서는, 비교하기 전에 변수를 전환 해줘야 합니다.
age = Number(age);
if (isNaN(age)) {
voteable = "Error in input";
} else {
voteable = (age < 18) ? "Too young" : "Old enough";
}
JavaScript Bitwise Operators
자바스크립트 비트 연산자
Bit operators work on 32-bit numbers.
Any numeric operand in the operation is converted into a 32-bit number.
The result is converted back to a JavaScript number.
비트 연산자는 32비트 숫자로 작동합니다.
동작에 있어서 어떤 수 피연산 함수는 32비트 숫자로 변환됩니다.
그 결과는 자바스크립트의 숫자로 변환되어 돌아옵니다.
Example x = 5 & 1; The result in x: 1
Operator Description Example Same as Result Decimal & AND x = 5 & 1 0101 & 0001 0001 1 | OR x = 5 | 1 0101 | 0001 0101 5 ~ NOT x = ~ 5 ~0101 1010 10 ^ XOR x = 5 ^ 1 0101 ^ 0001 0100 4 << Left shift x = 5 << 1 0101 << 1 1010 10 >> Right shift x = 5 >> 1 0101 >> 1 0010 2
The examples above use 4 bits unsigned examples. But JavaScript uses 32-bit signed numbers.
Because of this, in JavaScript, ~ 5 will not return 10. It will return -6.
~00000000000000000000000000000101 will return 11111111111111111111111111111010
위에 예제에서는 부호가 없는 예제는 4비트를 사용합니다. 하지만 자바스크립트는 부호가 있는 숫자는 32비트를 사용합니다.
이 때문에, 자바스크립트 안에서는 ~5는 10을 반환하지 않습니다. 그것은 -6 으로 반환합니다.
~5(0101) 반대값 10(1010)은 4비트에서의 결과값 32비트에서의 결과 값: ~5(00000000000000000000000000000101) -6(11111111111111111111111111111010)
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5] [연습문제6]
JavaScript If…Else Statements
자바스크립트 if…Else문
Conditional statements are used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
조건문은 다양한 조건을 기반으로 하는 동작을 하기 위해서 사용됩니다.
Conditional Statements
조건문
Very often when you write code, you want to perform different actions for different decisions.
You can use conditional statements in your code to do this.
In JavaScript we have the following conditional statements:
- Use if to specify a block of code to be executed, if a specified condition is true
- Use else to specify a block of code to be executed, if the same condition is false
- Use else if to specify a new condition to test, if the first condition is false
- Use switch to specify many alternative blocks of code to be executed
당신이 코드를 작성할때 매우 자주, 다른 조건에서 결정을 하고싶어 합니다.
당신의 코드에서 조건문을 사용할 수 있습니다.
우리는 자바스크립트안에 다음과 같은 조건문을 가질 수 있습니다.
- if는 코드범위에 명시된 작업의 조건이 만약 참일경우에 작업을 수행하기 위해 사용합니다.
- else는 코드범위에 명시된 작업의 조건이 만약 false와 같다면 수행사기 위해 사용합니다.
- else if는 새로운 조건 지정하고 테스트 하기위서 만약 첫번째 조건이 false일 경우에 사용 합니다.
- switch는 많은 조건의 코드 범위에서 명시된 조건을 선택하여 실행하기 위해 사용합니다.
The if Statement
if문
Use the if statement to specify a block of JavaScript code to be executed if a condition is true.
if 문은 자바스크립트 코드범위안에 명시된 조건이 참 일때 실행 되기 위해서 사용합니다.
Syntax 문법
if (condition) {
block of code to be executed if the condition is true
}
Note that if is in lowercase letters. Uppercase letters (If or IF) will generate a JavaScript error.
참고하세요 if는 소문자 입니다. 대문자일 경우(If나 IF)에는 자바스크립트는 오류를 발생시킵니다.
Example
Make a "Good day" greeting if the hour is less than 18:00:
if (hour < 18) {
greeting = "Good day";
}
The result of greeting will be:
Good day
The else Statement
else문
Use the else statement to specify a block of code to be executed if the condition is false.
else문은 코드범위에서 명시된 조건이 만약 false인 경우에 실행하기 위해 사용합니다.
if (condition) {
block of code to be executed if the condition is true
} else {
block of code to be executed if the condition is false
}
Example
If the hour is less than 18, create a "Good day" greeting, otherwise "Good evening":
if (hour < 18) {
greeting = "Good day";
} else {
greeting = "Good evening";
}
The result of greeting will be:
Good day
The else if Statement
else if문
Use the else if statement to specify a new condition if the first condition is false.
else if문은 첫번째 조건이 false인 경우에 새로운 조건을 명시하기 위해 사용합니다.
Syntax 문법
if (condition1) {
block of code to be executed if condition1 is true
} else if (condition2) {
block of code to be executed if the condition1 is false and condition2 is true
} else {
block of code to be executed if the condition1 is false and condition2 is false
}
Example
If time is less than 10:00, create a "Good morning" greeting, if not, but time is less than 20:00, create a "Good day" greeting, otherwise a "Good evening":
if (time < 10) {
greeting = "Good morning";
} else if (time < 20) {
greeting = "Good day";
} else {
greeting = "Good evening";
}
The result of greeting will be:
Good morning
More Examples
Random link This example will write a link to either W3Schools or to the World Wildlife Foundation (WWF). By using a random number, there is a 50% chance for each of the links.
위의 링크 예제는 50%의 확률로 세계적인 동물 사이트나 W3Schools중 하나를 랜덤으로 링크로 나타내 주는 예제 입니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5] [연습문제6]
JavaScript Switch Statement
자바스크립트 Switch문
The switch statement is used to perform different actions based on different conditions.
switch문은 다양한 조건에 맞게 실행되기 위해서 사용합니다.
The JavaScript Switch Statement
자바스크립트 Switch문
Use the switch statement to select one of many blocks of code to be executed.
많은 조건 중에서 하나의 코드를 표현하기 위해서 switch문을 사용합니다.
Syntax 문법
switch(expression) {
case n:
code block
break;
case n:
code block
break;
default:
default code block
}
This is how it works:
- The switch expression is evaluated once.
- The value of the expression is compared with the values of each case.
- If there is a match, the associated block of code is executed.
동작방법:
- switch표현은 한번씩 평가됩니다.
- 표현식의 값은 각각의 경우에 값을 비교합니다.
- 만약 맞는 것이 존재한다면, 관련된 블록의 코드를 실행 할 것입니다.
Example
The getDay() method returns the weekday as a number between 0 and 6. (Sunday=0, Monday=1, Tuesday=2 ..)
Use the weekday number to calculate weekday name:
switch (new Date().getDay()) {
case 0:
day = "Sunday";
break;
case 1:
day = "Monday";
break;
case 2:
day = "Tuesday";
break;
case 3:
day = "Wednesday";
break;
case 4:
day = "Thursday";
break;
case 5:
day = "Friday";
break;
case 6:
day = "Saturday";
break;
}
The result of day will be:
Thursday
The break Keyword
break키워드
When the JavaScript code interpreter reaches a break keyword, it breaks out of the switch block.
This will stop the execution of more code and case testing inside the block.
When a match is found, and the job is done, it’s time for a break.
There is no need for more testing.
그것은 자바스크립트 코드를 해석하다가 swich블록 중에서 break키워드에 도달 했을 때 정지합니다.
이것은 더 많은 코드와 case블록 내부의 테스트를 중단 시킵니다.
맞는 것을 찾았을 때, 그리고 일이 끝날때, 그것을 중단시킵니다.
그것들은 그 이상의 테스트를 필요로 하지 않습니다.
The default Keyword
default키워드
The default keyword specifies the code to run if there is no case match:
default 키워드는 코드를 실행하다가 만약 그것들과 맞는 경우가 없을때 명시합니다.
Example
The getDay() method returns the weekday as a number between 0 and 6.
If today is neither Saturday (6) nor Sunday (0), write a default message:
switch (new Date().getDay()) {
case 6:
text = "Today is Saturday";
break;
case 0:
text = "Today is Sunday";
break;
default:
text = "Looking forward to the Weekend";
}
The result of text will be:
Looking forward to the Weekend
Common Code and Fall-Through
공통 코드와 실패로 끝난
Sometimes, in a switch block, you will want different cases to use the same code, or fall-through to a common default.
Note from the next example, that cases can share the same code block, and that the default case does not have to be the last case in a switch block:
때때로, 스위치 블록에 동일한 코드를 사용하거나 공통 기본으로 서로 다른 경우를 원할 것 입니다.
다음 예제는, 동일한 코드 불록은 공유할 수 있고 스위치 블록 내의 마지막 경우로 하지 않습니다.
Example
switch (new Date().getDay()) {
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
default:
text = "Looking forward to the Weekend";
break;
case 4:
case 5:
text = "Soon it is Weekend";
break;
case 0:
case 6:
text = "It is Weekend";
}
If default is not the last case in the switch block, remember to end it with a break.
기본적으로 default는 switch블록의 case안에서 마지막이 아닐경우에, 끝과 중지로 기억합니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4]
JavaScript For Loop
자바스크립트 For루프
Loops can execute a block of code a number of times.
블럭 코드를 몇번이고 반복적으로 실행하는게 가능합니다.
JavaScript Loops
자바스크립트 루프
Loops are handy, if you want to run the same code over and over again, each time with a different value.
Often this is the case when working with arrays:
당신은 각각의 다른 값으로 처음부터 같은 코드를 다시 반복해서 편리하게 사용하길 원합니다.
보통 배열로 작업하는 경우는 다음과 같습니다:
Instead of writing:
text += cars[0] + "<br>";
text += cars[1] + "<br>";
text += cars[2] + "<br>";
text += cars[3] + "<br>";
text += cars[4] + "<br>";
text += cars[5] + "<br>";
You can write:
for (i = 0; i < cars.length; i++) {
text += cars[i] + "<br>";
}
Different Kinds of Loops
Loop의 약간 다른 차이
JavaScript supports different kinds of loops:
- for - loops through a block of code a number of times
- for/in - loops through the properties of an object
- while - loops through a block of code while a specified condition is true
- do/while - also loops through a block of code while a specified condition is true
자바스크립트는 약간 다른 차이의 loop를 지원 합니다:
- for - 코드 블록을 통하여 몇번이고 반복합니다.
- for/in - 오브젝트의 성질을 통하여 반복합니다.
- while - 명시된 조건이 true일 동안에 코드 블록을 반복합니다.
- do/while - 또한 코드블록을 통해 명시된 조건이 참일 동안에 반복합니다.
The For Loop
For 루프
The for loop is often the tool you will use when you want to create a loop.
The for loop has the following syntax:
for반복은 보통 당신이 새로운 반복을 하기를 원할 때 도구로 사용 됩니다.
다음은 for반복에대한 문법 입니다.
for (statement 1; statement 2; statement 3) {
code block to be executed
}
Statement 1 is executed before the loop (the code block) starts.
Statement 2 defines the condition for running the loop (the code block).
Statement 3 is executed each time after the loop (the code block) has been executed.
Statement 1은 루프(코드 블록)가 시작되기 전에 실행 됩니다. Statement 2는 루프(코드 블록)를 실행하기 위한 조건 입니다. Statement 3은 루프(코드 블록)가 실행 된 후마다 실행 됩니다.
Example
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
text += "The number is " + i + "<br>";
}
From the example above, you can read:
Statement 1 sets a variable before the loop starts (var i = 0).
Statement 2 defines the condition for the loop to run (i must be less than 5).
Statement 3 increases a value (i++) each time the code block in the loop has been executed.
위의 예에서 당신은 읽을 수 있었습니다: Statement 1은 변수 값에 루프의 시작(var i =0)을 먼져 저장합니다. Statement 2는 실행하는 루프의 조건을 정의(i는 5보다 작을때) Statement 3은 값이 블록 코드에서 반복적으로 실행 될 각각의 시간을 증가(i++) 시킵니다.
Statement 1
Statement 1
Normally you will use statement 1 to initiate the variable used in the loop (i = 0).
This is not always the case, JavaScript doesn’t care. Statement 1 is optional.
You can initiate many values in statement 1 (separated by comma):
당신은 보통은 statement1은 루프에 사용할 변수를 지정합니다.(i = 0)
항상 그런것은 아닙니다, 자바스크립트는 상관하지 않습니다. Statement1은 선택 사항입니다.
당신은 쉼표로 statement1의 많은 값들을 구분 할 수 있습니다.
Example
for (i = 0, len = cars.length, text = ""; i < len; i++) {
text += cars[i] + "<br>";
}
And you can omit statement 1 (like when your values are set before the loop starts):
그리고 당신은 statement1을 생략하는것이 가능합니다.(반복이 시작되기 전에 설정되는 경우에는)
Example
var i = 2;
var len = cars.length;
var text = "";
for (; i < len; i++) {
text += cars[i] + "<br>";
}
Statement 2
Statement 2
Often statement 2 is used to evaluate the condition of the initial variable.
This is not always the case, JavaScript doesn’t care. Statement 2 is also optional.
If statement 2 returns true, the loop will start over again, if it returns false, the loop will end.
If you omit statement 2, you must provide a break inside the loop. Otherwise the loop will never end. This will crash your browser. Read about breaks in a later chapter of this tutorial.
보통 statement2는 초기 변수의 상태를 평가하는데 사용됩니다.
항상 그런것은 아닙니다, 자바스크립트는 상관하지 않습니다. Statement2또한 선택사항 입니다.
만약 statement2가 true 를 반환하면, 반복문은 다시 시작됩니다, 만약 false를 반환하면, 루프는 끝날 것입니다.
만약 statement2를 생략한다면, 당신은 반복 안에 break를 제공 해야합니다. 아닐경우에는 그것은 끝없이 반복할 것입니다.
이 브라우저는 충돌합니다. 이 튜토리얼의 이후에 break에 대해서 읽어 보십시오.
Statement 3
Statement 3
Often statement 3 increases the initial variable.
This is not always the case, JavaScript doesn’t care, and statement 3 is optional.
Statement 3 can do anything like negative increment (i–), positive increment (i = i + 15), or anything else.
Statement 3 can also be omitted (like when you increment your values inside the loop):
보통의 statement3은 초기 변수를 증가 시킵니다.
항상 그런것은 아닙니다, 자바스크립트는 상관하지 않고, statement3은 선택사항 입니다.
statement3은 음의 증가, 양의증가 또는 그밖에 다른 것도 할 수 있습니다.
statement3는 (당신의 값을 루프 안에서 증가 시키는 것과 같이) 생략할 수 있습니다.
Example
var i = 0;
var len = cars.length;
for (; i < len; ) {
text += cars[i] + "<br>";
i++;
}
The For/In Loop
For/In 루프
The JavaScript for/in statement loops through the properties of an object:
for/in문은 자바스크립트의 객체의 속성을 통해서 반복됩니다.
Example
var person = {fname:"John", lname:"Doe", age:25};
var text = "";
var x;
for (x in person) {
text += person[x];
}
The While Loop
While 루프
The while loop and the do/while loop will be explained in the next chapter.
While과 do/while 루프는 다음 장에서 설명 하겠습니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4]
JavaScript While Loop
자바스크립트 while 반복
Loops can execute a block of code as long as a specified condition is true.
명시된 조건이 true일동안 블록 코드를 반복해서 실행하는 것이 가능합니다.
The While Loop
While 루프
The while loop loops through a block of code as long as a specified condition is true.
while루프는 명시된 조건이 true일 동안 코드 블록을 반복 합니다.
Syntax 문법
while (condition) {
code block to be executed
}
Example
In the following example, the code in the loop will run, over and over again, as long as a variable (i) is less than 10:
예제
다음 예제는, 변수i가 10보다 작을 동안에, 루프의 코드가 실행되고, 여러번 다시 반복되는 예제 입니다.
Example
while (i < 10) {
text += "The number is " + i;
i++;
}
If you forget to increase the variable used in the condition, the loop will never end. This will crash your browser.
만약 당신이 변수를 증가시키는 조건을 사용하는 것을 잊었다면, 루프는 종료되지 않습니다. 당신의 브라우저는 충돌합니다.
The Do/While Loop
Do/While 루프
The do/while loop is a variant of the while loop. This loop will execute the code block once, before checking if the condition is true, then it will repeat the loop as long as the condition is true.
do/while루프는 while루프에서 변환된 것 입니다. 이 루프는 코드블록을 한번 실행하기 전에 만약 조건이 true인지 확인하고, 조건이 true일 동안에 반복합니다.
Syntax
do {
code block to be executed
}
while (condition);
Example
The example below uses a do/while loop. The loop will always be executed at least once, even if the condition is false, because the code block is executed before the condition is tested:
예제
이 아래의 예제는 do/while루프를 사용하였습니다. 조건이 테스트전에 코드블록이 실행 되기 때문에, 이 루프는 조건이 false일 경우에도 적어도 1번은 실행 합니다.
Example
do {
text += "The number is " + i;
i++;
}
while (i < 10);
Do not forget to increase the variable used in the condition, otherwise the loop will never end!
조건에 대한 변수의 증가 값을 사용하는 것을 잊으면 안됩니다, 그렇지 않는다면 루프는 절대로 끝나지 않습니다.
Comparing For and While
For과 While 비교하기
If you have read the previous chapter, about the for loop, you will discover that a while loop is much the same as a for loop, with statement 1 and statement 3 omitted.
The loop in this example uses a for loop to collect the car names from the cars array:
당신은 이전의 장에서 for loop에 대해서 읽었다면, 당신은 satament1과 statement3의 생략과 같은 while loop와 같은점을 발견 했을 것 입니다.
이 루프 예제는 for loop안에서 차 이름을 수집하는 차 배열에 대한 예제 입니다.
Example
var cars = ["BMW", "Volvo", "Saab", "Ford"];
var i = 0;
var text = "";
for (;cars[i];) {
text += cars[i] + "
";
i++;
}
The loop in this example uses a while loop to collect the car names from the cars array:
이 루프 예제는 while루프를 사용해서 차 이름을 차 배열에서 반복적으로 가지고 오는 예제입니다.
Example
var cars = ["BMW", "Volvo", "Saab", "Ford"];
var i = 0;
var text = "";
while (cars[i]) {
text += cars[i] + "
";
i++;
}
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5]
JavaScript Break and Continue
자바스크립트의 중단과 계속
The break statement “jumps out” of a loop.
The continue statement “jumps over” one iteration in the loop.
break statement는 루프에서 밖으로 나가집니다.
continue statement는 루프에서 하나씩 반복을 통해 넘어갑니다.
The Break Statement
Break Statement
You have already seen the break statement used in an earlier chapter of this tutorial. It was used to “jump out” of a switch() statement.
The break statement can also be used to jump out of a loop.
The break statement breaks the loop and continues executing the code after the loop (if any):
당신은 이미 이튜토리얼 이전에 break statement에 대해서 switch() statement의 반복을 통하여 본적 있습니다.
break statement는 루프를 빠져 나올때도 사용이 가능합니다.
break statement는 루프를 중단하거나 루프 다음의 코드를 실행 합니다.
Example
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i === 3) { break; }
text += "The number is " + i + "<br>";
}
The Continue Statement
Continue Statement
The continue statement breaks one iteration (in the loop), if a specified condition occurs, and continues with the next iteration in the loop.
This example skips the value of 3:
continue statement는 한번의 반복(루프 안에서)을 마치고, 만약 명시된 조건의 일이 일어나면, 계속 다음 루프를 반복합니다.
이 예제는 3의 값을 넘어가는 예제입니다.
Example
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i === 3) { continue; }
text += "The number is " + i + "<br>";
}
JavaScript Labels
자바스클비트 라벨
To label JavaScript statements you precede the statements with a label name and a colon:
JavaScript statements의 라벨을 지정하려면 statements의 앞에 이름과 콜론을 선언합니다.
label: statements
The break and the continue statements are the only JavaScript statements that can “jump out of” a code block.
break와 continue statements는 자바스크립트 statements들의 코드 블록만 나갈수 있습니다.
Syntax: 문법
break labelname; continue labelname;
The continue statement (with or without a label reference) can only be used to skip one loop iteration.
The break statement, without a label reference, can only be used to jump out of a loop or a switch.
With a label reference, the break statement can be used to jump out of any code block:
continue statement는 오직 하나의 루프 반복을 건너 뛸 경우에 사용이 가능합니다.
break statement는, 라벨을 참조하지 않고, 오직 루프를 빠져나오거나 switch에서 사용이 가능합니다.
라벨을 참고하여, break statement는 모든 코드 블록을 빠져나올때 사용합니다.
Example
var cars = ["BMW", "Volvo", "Saab", "Ford"];
list: {
text += cars[0] + "
";
text += cars[1] + "
";
text += cars[2] + "
";
text += cars[3] + "
";
break list;
text += cars[4] + "
";
text += cars[5] + "
";
}
A code block is a block of code between { and }.
코드블록은 {와} 사이에 코드블록 입니다.
Test Yourself with Exercises!
연습문제로 자신을 테스트!
[연습문제1] [연습문제2] [연습문제3] [연습문제4] [연습문제5]
JavaScript Type Conversion
자바스크립트 타입 변환
Number() converts to a Number, String() converts to a String, Boolean() converts to a Boolean.
Number()를 숫자로 변환, String()을 문자로 변환, Boolean()을 논리형으로 변환합니다.
JavaScript Data Types
자바스크립트 날짜 형식
In JavaScript there are 5 different data types that can contain values:
자바스크립트는 5가지의 다른 데이터 형식으로 값이 들어 있습니다.
- string 문자형
- number 숫자형
- boolean 논리형
- object 오브젝트
- functions 함수
There are 3 types of objects:
오브젝트는 3가지 타입이 존재합니다.
- Object
- Date
- Array
And 2 data types that cannot contain values:
그리고 2가지의 데이터 타입으로 존재하지 않는 값이 들어갑니다.
- null
- undefined
The typeof Operator
typeof연산자
You can use the typeof operator to find the data type of a JavaScript variable.
당신은 typeof연산자를 사용해서 자바스크립트 변수의 데이터 형식을 찾을 수 있습니다.
Example
typeof "John" // Returns string
typeof 3.14 // Returns number
typeof NaN // Returns number
typeof false // Returns boolean
typeof [1,2,3,4] // Returns object
typeof {name:'John', age:34} // Returns object
typeof new Date() // Returns object
typeof function () {} // Returns function
typeof myCar // Returns undefined (if myCar is not declared)
typeof null // Returns object
Please observe:
지켜야할 사항:
- The data type of NaN is number
- The data type of an array is object
- The data type of a date is object
- The data type of null is object
-
The data type of an undefined variable is undefined
- NaN의 데이터 형식은 숫자 입니다.
- 배열의 데이터형식은 오브젝트 입니다.
- 날짜의 데이터 형식은 오브젝트 입니다.
- null의 데이터 형식은 오브젝트 입니다.
- 변수가 undefined이면 데이터 형식은 undefined입니다.
You cannot use typeof to determine if a JavaScript object is an array (or a date).
자바스크립트가 배열(또는 날짜)인 경우에는 typeof를 사용해도 알 수 없습니다.
The Data Type of typeof
typeof의 데이터 형식
The typeof operator is not a variable. It is an operator. Operators ( + - * / ) do not have any data type.
But, the typeof operator always returns a string containing the type of the operand.
typeof연산자는 변수가 아닙니다. 이것은 연산자 입니다. 연산자이지만 ( + = * /)데이터 형식을 가지고 있지는 않습니다.
The constructor Property
생성자 속성
The constructor property returns the constructor function for all JavaScript variables.
모든 자바스크립트 변수의 생성자 함수는 생성자 속성을 반환합니다.
Example
"John".constructor // Returns function String() { [native code] }
(3.14).constructor // Returns function Number() { [native code] }
false.constructor // Returns function Boolean() { [native code] }
[1,2,3,4].constructor // Returns function Array() { [native code] }
{name:'John', age:34}.constructor // Returns function Object() { [native code] }
new Date().constructor // Returns function Date() { [native code] }
function () {}.constructor // Returns function Function(){ [native code] }
You can check the constructor property to find out if an object is an Array (contains the word “Array”):
당신의 객체가 배열(단어배열 포함)인 경우에 생성자 속성을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Example
function isArray(myArray) {
return myArray.constructor.toString().indexOf("Array") > -1;
}
You can check the constructor property to find out if an object is a Date (contains the word “Date”):
당신은 객체가 날짜(단어날짜 포함)인 경우에 생성자 속성을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Example
function isDate(myDate) {
return myDate.constructor.toString().indexOf("Date") > -1;
}
JavaScript Type Conversion
자바스크립트 형변환
JavaScript variables can be converted to a new variable and another data type:
자바스크립트 변수는 새로운 변수와 다른 데이터 형식으로 형변환이 가능합니다.
- By the use of a JavaScript function
-
Automatically by JavaScript itself
- 자바스크립트 함수를 사용하여
- 자바스크립트 스스로 자동적으로
Converting Numbers to Strings
숫자를 문자로 변환
The global method String() can convert numbers to strings.
It can be used on any type of numbers, literals, variables, or expressions:
전역 메소드 String()으로 숫자를 문자로 변환할 수 있습니다.
그것은 아무런 숫자, 변수, 정수, 표현 형식에 사용 가능합니다.
Example String(x) // returns a string from a number variable x String(123) // returns a string from a number literal 123 String(100 + 23) // returns a string from a number from an expression
The Number method toString() does the same.
숫자는 toString()와 방법은 같습니다.
Example x.toString() (123).toString() (100 + 23).toString()
In the chapter Number Methods, you will find more methods that can be used to convert numbers to strings:
이번 장에서 숫자 메소드는, 당신이 많은 방법을 찾을 수 있습니다 숫자에서 문자로 변경하는
Method Description toExponential() Returns a string, with a number rounded and written using exponential notation. toFixed() Returns a string, with a number rounded and written with a specified number of decimals. toPrecision() Returns a string, with a number written with a specified length
Converting Booleans to Strings
논리형을 문자로 변환
The global method String() can convert booleans to strings.
전역 메소드 String()으로 논리형을 문자로 변환할 수 있습니다.
String(false) // returns "false" String(true) // returns "true"
The Boolean method toString() does the same.
논리형은 toString()과 방법은 같습니다.
false.toString() // returns "false" true.toString() // returns "true"
Converting Dates to Strings
날짜를 문자로 변환
The global method String() can convert dates to strings.
전역 메소드 String()으로 날짜를 문자로 변환할 수 있습니다.
String(Date()) // returns Thu Jul 17 2014 15:38:19 GMT+0200 (W. Europe Daylight Time)
The Date method toString() does the same.
날짜 메소드는 toString()과 동일한 작업을 합니다.
Example Date().toString() // returns Thu Jul 17 2014 15:38:19 GMT+0200 (W. Europe Daylight Time)
In the chapter Date Methods, you will find more methods that can be used to convert dates to strings:
날짜메소드 장에서, 당신은 날짜에서 문자열로 변환하는데 사용 할 수 있는 방법을 찾을 수 있을 것 입니다.
Method Description getDate() Get the day as a number (1-31) getDay() Get the weekday a number (0-6) getFullYear() Get the four digit year (yyyy) getHours() Get the hour (0-23) getMilliseconds() Get the milliseconds (0-999) getMinutes() Get the minutes (0-59) getMonth() Get the month (0-11) getSeconds() Get the seconds (0-59) getTime() Get the time (milliseconds since January 1, 1970)
Converting Strings to Numbers
문자를 숫자로 변환
The global method Number() can convert strings to numbers.
Strings containing numbers (like “3.14”) convert to numbers (like 3.14).
Empty strings convert to 0.
Anything else converts to NaN (Not a number).
전역 메소드 Number()로 문자를 숫자로 변환 할수 있습니다.
숫자를 포함한 문자열은 숫자로 변환합니다.
빈 문자열은 0으로 변환합니다.
다른 것은 NaN(숫자가 아닌)으로 변환합니다.
Number("3.14") // returns 3.14
Number(" ") // returns 0
Number("") // returns 0
Number("99 88") // returns NaN
In the chapter Number Methods, you will find more methods that can be used to convert strings to numbers:
Number메소드 장 안에서, 당신은 문자를 숫자로 변환하는 방법에 대해서 더많은 방법을 찾을 수 있을 것 입니다.
Method Description parseFloat() Parses a string and returns a floating point number parseInt() Parses a string and returns an integer
The Unary + Operator
단항 + 연산자
The unary + operator can be used to convert a variable to a number:
단항 + 연산자는 변수를 숫자로 변환하여 사용이 가능합니다.
Example var y = "5"; // y is a string var x = + y; // x is a number
If the variable cannot be converted, it will still become a number, but with the value NaN (Not a number):
변수는 숫자로 변환할 수 없는경우, 그것은 여전히 NaN값과 숫자가 될 것입니다.
Example var y = "John"; // y is a string var x = + y; // x is a number (NaN)
Converting Booleans to Numbers
논리형을 숫자로 변환
The global method Number() can also convert booleans to numbers.
전역 메소드 Number()또한 논리형을 숫자로 변환할 수 있습니다.
Number(false) // returns 0 Number(true) // returns 1
Converting Dates to Numbers
날짜를 숫자로 변환
The global method Number() can be used to convert dates to numbers.
전역 메소드 Number()는 날짜를 숫자로 변환하여 사용할 수 있습니다.
d = new Date(); Number(d) // returns 1404568027739
The date method getTime() does the same.
날짜 메소드도 getTime()과 동작은 같습니다.
d = new Date(); d.getTime() // returns 1404568027739
Automatic Type Conversion
자동 형변환
When JavaScript tries to operate on a “wrong” data type, it will try to convert the value to a “right” type.
The result is not always what you expect:
자바스크립트에서 데이터 형식이 틀린 작동을 하려고 할때, 그것은 오른쪽에 있는 값으로 변환을 시도할 것 입니다.
5 + null // returns 5 because null is converted to 0 "5" + null // returns "5null" because null is converted to "null" "5" + 2 // returns 52 because 2 is converted to "2" "5" - 2 // returns 3 because "5" is converted to 5 "5" * "2" // returns 10 because "5" and "2" are converted to 5 and 2
Automatic String Conversion
자동 문자열 변환
JavaScript automatically calls the variable’s toString() function when you try to “output” an object or a variable:
함수에서 오브젝트나 변수를 출력하려고 할때 자바스크립트는 자동으로 변수에 toString()을 호출합니다.
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = myVar;
// if myVar = {name:"Fjohn"} // toString converts to "[object Object]"
// if myVar = [1,2,3,4] // toString converts to "1,2,3,4"
// if myVar = new Date() // toString converts to "Fri Jul 18 2014 09:08:55 GMT+0200"
Numbers and booleans are also converted, but this is not very visible:
숫자나 논리형 또한 변환됩니다, 하지만 이것은 보이지 않을 것 입니다.
// if myVar = 123 // toString converts to "123" // if myVar = true // toString converts to "true" // if myVar = false // toString converts to "false"
JavaScript Type Conversion Table
자바스크립트 형변환 표
This table shows the result of converting different JavaScript values to Number, String, and Boolean:
이 테이블은 숫자, 문자열 및 논리형 자바스크립트 값을 변환한 결과 값 입니다.
Original Converted Converted Converted
Value to Number to String to Boolean
false 0 "false" false
true 1 "true" true
0 0 "0" false
1 1 "1" true
"0" 0 "0" true
"1" 1 "1" true
NaN NaN "NaN" false
Infinity Infinity "Infinity" true
-Infinity -Infinity "-Infinity" true
"" 0 "" false
"20" 20 "20" true
"twenty" NaN "twenty" true
[ ] 0 "" true
[20] 20 "20" true
[10,20] NaN "10,20" true
["twenty"] NaN "twenty" true
["ten","twenty"] NaN "ten,twenty" true
function(){} NaN "function(){}" true
{ } NaN "[object Object]" true
null 0 "null" false
undefined NaN "undefined" false
Values in quotes indicate string values.
Yellow zones values indicate values (some) programmers might not expect.
따옴표 값은 문자열을 나타냅니다.
노란색 영역의 값들은 프로그래머의 예상과 다를 수 있다는 것을 나타냅니다.
JavaScript Regular Expressions
자바스크립트 정규 표현식
A regular expression is a sequence of characters that forms a search pattern.
The search pattern can be used for text search and text replace operations.
정규 표현식은 문자의 순서나 패턴 형태에 대해서 형성 됩니다.
검색 패턴을 사용해서 문자 검색이나 문자 순서를 변경할 수 있습니다.
What Is a Regular Expression?
정규 표현식이란 무엇인가?
A regular expression is a sequence of characters that forms a search pattern.
When you search for data in a text, you can use this search pattern to describe what you are searching for.
A regular expression can be a single character, or a more complicated pattern.
Regular expressions can be used to perform all types of text search and text replace operations.
정규 표현식은 문자의 순서나 패턴 형식에 대해서 형성 됩니다.
데이터 안의 문자를 검색할 때, 당신은 당신이 찾는것을 위하여 검색 패턴을 사용할 수 있습니다.
정규 표현식은 단일 문자나, 복잡한 패턴도 가능합니다.
정규 표현식은 모든 형식의 문자 검색이나 문자 순서를 변경할 수 있습니다.
Syntax /pattern/modifiers; Example var patt = /w3schools/i;
Example explained: /w3schools/i is a regular expression. w3schools is a pattern (to be used in a search). i is a modifier (modifies the search to be case-insensitive).
예제 설명:
/w3schools/i는 정규 표현식 입니다.
w3schools는 (검색할때 사용하는)패턴입니다.
i수식어는 (대소문자를 구별 하지 않도록 하는 수식어) 입니다.
Using String Methods
String메소드 사용
In JavaScript, regular expressions are often used with the two string methods: search() and replace().
The search() method uses an expression to search for a match, and returns the position of the match.
The replace() method returns a modified string where the pattern is replaced.
자바스크립트 에서 정규 표현식은 보통 2개의 string메소드: search()와 replace()를 같이 사용합니다.
search()메소드는 표현식 검색의 일치나, 일치된 위치를 반환합니다.
replace()메소드는 문자열에 패턴을 대신해서 수정합니다.
Using String search() With a Regular Expression
문자열 search()와 정규 표현식 사용
Example Use a regular expression to do a case-insensitive search for "w3schools" in a string: var str = "Visit W3Schools"; var n = str.search(/w3schools/i); The result in n will be: 6
Using String search() With String
문자열 search()와 문자열 사용
The search method will also accept a string as search argument. The string argument will be converted to a regular expression:
search메소드는 검색인자로 문자열을 받아들입니다. 문자열 인수는 정규 표현식으로 변환됩니다.
Example
Use a string to do a search for "W3schools" in a string:
var str = "Visit W3Schools!";
var n = str.search("W3Schools");
Use String replace() With a Regular Expression
정규 표현식으로 문자열 replace() 대체 사용
Example Use a case insensitive regular expression to replace Microsoft with W3Schools in a string: var str = "Visit Microsoft!"; var res = str.replace(/microsoft/i, "W3Schools"); The result in res will be: Visit W3Schools!
Using String replace() With a String
문자열로 문자열 replace() 대체 사용
The replace() method will also accept a string as search argument:
replace()메소드는 검색인자로 문자열을 받아들입니다.
var str = "Visit Microsoft!";
var res = str.replace("Microsoft", "W3Schools");
Did You Notice?
알아채셨나요?
Regular expression arguments (instead of string arguments) can be used in the methods above. Regular expressions can make your search much more powerful (case insensitive for example).
(문자열 인수 대신)정규 표현식 인수는 위의 방법으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
정규 표현식은 (예를 들어 대소문자를) 당신이 더 정확하게 검색할 수 있도록 만들어 줍니다.
Regular Expression Modifiers
정규 표현식 수식어
Modifiers can be used to perform case-insensitive more global searches:
수식어는 전역에서 대소문자를 구별해서 검색을 실핼할 수 있습니다.
Modifier Description i Perform case-insensitive matching g Perform a global match (find all matches rather than stopping after the first match) m Perform multiline matching i 대소문자를 구별하여 맞는 지를 수행합니다. g 전역에서 맞는지를 수행합니다.(오히려 모두 일치 했을때 보다 첫번째 일치 되는 것에서 정지 합니다.) m 여러 매칭을 수행합니다.
Regular Expression Patterns
정규 표현식 패턴들
Brackets are used to find a range of characters:
괄호는 범위로 문자를 찾는데 사용됩니다.
Expression Description [abc] Find any of the characters between the brackets [0-9] Find any of the digits between the brackets (x|y) Find any of the alternatives separated with | [abc] 괄호 사이의 문자를 찾습니다. [0-9] 괄호 사이의 숫자를 찾습니다. (x|y) |로 구분하여 맞는 값을 찾아냅니다.
Metacharacters are characters with a special meaning:
메타문자는 특별한 의미를 가진 문자 입니다.
Metacharacter Description \d Find a digit \s Find a whitespace character \b Find a match at the beginning or at the end of a word \uxxxx Find the Unicode character specified by the hexadecimal number xxxx \d 숫자를 찾습니다. \s 여백 문자를 찾습니다. \b 시작 또는 끝에서 일치하는 단어를 찾습니다. \uxxxx 16진수 xxxx에 의한 특정유니코드 문자를 찾습니다.
Quantifiers define quantities:
Quantifier Description n+ Matches any string that contains at least one n n* Matches any string that contains zero or more occurrences of n n? Matches any string that contains zero or one occurrences of n n+ 적어도 하나의n을 포함한 모든 문자열의 일치 n* n은 0개 이상의 항목을 포함하는 모든 문자열 일치 n? n개의 0또는 1개 항목을 포함하는 모든 문자열이 일치
Using the RegExp Object
정규식 객체 사용
In JavaScript, the RegExp object is a regular expression object with predefined properties and methods.
자바스크립트의 정규 표현식 객체는 미리정해진 속성과 방법의 정규식 객체입니다.
Using test()
test()사용
The test() method is a RegExp expression method.
It searches a string for a pattern, and returns true or false, depending on the result.
The following example searches a string for the character “e”:
test()메소드는 정규식 표현 방법입니다.
문자열의 패턴 검색 결과에 따라 true 또는 false를 반환합니다.
다음은 문자열의 문자”e”를 검색하는 예제 입니다.
Example
var patt = /e/;
patt.test("The best things in life are free!");
Since there is an "e" in the string, the output of the code above will be:
true
You don't have to put the regular expression in a variable first. The two lines above can be shortened to one:
/e/.test("The best things in life are free!");
Using exec()
exec()사용
The exec() method is a RegExp expression method.
It searches a string for a specified pattern, and returns the found text.
If no match is found, it returns null.
The following example searches a string for the character “e”:
exec()메소드는 정규식 표현 방법입니다.
문자열의 명시된 패턴을 검색해서, 찾은 문자를 반환합니다.
만약 일치하는 부분이 없다면, null을 반환합니다.
다음은 문자열의 문자”e”를 검색하는 예제입니다.
Example 1
/e/.exec("The best things in life are free!");
Since there is an "e" in the string, the output of the code above will be:
e
Complete RegExp Reference
완벽한 정규식 참조
For a complete reference, go to our Complete JavaScript RegExp Reference.
The reference contains descriptions and examples of all RegExp properties and methods.
필요한 모든 것이 갖춰진 우리의 자바스크립트 정규식 Reference 참조
reference에는 모든 정규식의 속성과 메소드에 대한 설명과 예제가 들어 있습니다.
JavaScript Errors - Throw and Try to Catch
자바스크립트 오류 - Throw와 Try to Catch
The try statement lets you test a block of code for errors.
The catch statement lets you handle the error.
The throw statement lets you create custom errors.
The finally statement lets you execute code, after try and catch, regardless of the result.
try구문으로 당신은 코드블록의 오류를 테스트 할 수 있습니다.
catch 구문으로 당신은 오류를 처리 할 수 있습니다.
throw구문으로 당신은 오류를 지정하여 만들 수 있습니다.
finally구문으로 당신의 try와 catch의 결과가 어떻든 간에 코드를 실행 합니다.
Errors Will Happen!
무슨 오류가 일어날 것인가!
When executing JavaScript code, different errors can occur.
Errors can be coding errors made by the programmer, errors due to wrong input, and other unforeseeable things:
자바스크립트 코드를 실행할때, 또다른 오류가발생 할 수 있습니다.
오류는 프로그래머에 의해 만들어진 오류로 인하여 잘못된 입력 오류 및 예상불가능한 일을 할 수 있습니다.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
try {
adddlert("Welcome guest!");
}
catch(err) {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = err.message;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
In the example above we have made a typo in the code (in the try block).
The catch block catches the error, and executes code to handle it.
위의 예제에서 우리는 오타를 만들어 냈습니다. (try블록안에) catch블록이 이러한 오류를 찾아내기 위하여 실행합니다.
JavaScript try and catch
자바스크립트 try와 catch
The try statement allows you to define a block of code to be tested for errors while it is being executed.
The catch statement allows you to define a block of code to be executed, if an error occurs in the try block.
The JavaScript statements try and catch come in pairs:
try구문 당신이 그것이 실행되는 동안 오류를 테스크할 코드 블록을 정의 할 수 있습니다.
try블록에서 오류가 발생 하였을 경우 catch구문은 당신은 코드블록이 실행 될 수 있도록 정의 할 수 있습니다.
자바스크립트 구문의 try와 catch는 한쌍 입니다.
try {
Block of code to try
}
catch(err) {
Block of code to handle errors
}
JavaScript can Raise Errors
자바스크립트는 오류를 발생 시킬 수 있습니다.
When an error occurs, JavaScript will normally stop, and generate an error message.
The technical term for this is: JavaScript will raise (or throw) an exception.
자바스크립트에서 오류가 발생했을때, 정상적으로 멈추고 오류 메시지를 발생 시킵니다.
기술적 용어 입니다: 자바스크립트는 예외를 발생 시킵니다.(또는 throw)
The throw Statement
throw 구문
The throw statement allows you to create a custom error.
Technically you can raise (throw) an exception.
The exception can be a JavaScript String, a Number, a Boolean or an Object:
throw구문을 사용하면 사용자 지정 오류를 만들어 낼 수 있습니다.
당신은 기술적으로 예외를 발생 시킬 수 있습니다.
자바스크립트 문자열과 숫자, 논리, 객체는 예외가 가능합니다.
throw "Too big"; // throw a text throw 500; // throw a number
If you use throw together with try and catch, you can control program flow and generate custom error messages.
만약 당신이 throw와 try와 catch를 같이 사용 한다면 당신은 프로그램의 흐름을 제어하고 사용자 지정 오류 메시지를 생성 할 수 있습니다.
Input Validation Example
입력 유효성 검사 예제
This example examines input. If the value is wrong, an exception (err) is thrown.
The exception (err) is caught by the catch statement and a custom error message is displayed:
이 예제는 예외를 검사 합니다. 예외가 있을 시 throw됩니다. 예외는 catch문에 의해서 사용자 지정 오류 메시지를 표시합니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Please input a number between 5 and 10:</p>vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv
<input id="demo" type="text">
<button type="button" onclick="myFunction()">Test Input</button>
<p id="message">v</p>
<script>
function myFunction() {
var message, x;
message = document.getElementById("message");
message.innerHTML = "";
x = document.getElementById("demo").value;
try {
if(x == "") throw "empty";
if(isNaN(x)) throw "not a number";
x = Number(x);
if(x < 5) throw "too low";
if(x > 10) throw "too high";
}
catch(err) {
message.innerHTML = "Input is " + err;
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
HTML Validation
HTML유효성 검사
The code above is just an example.
Modern browsers will often use a combination of JavaScript and built-in HTML validation, using predefined validation rules defined in HTML attributes:
위의 코드 예입니다. 현대의 브라우저들은 HTML속성 정의 사전 검증 규칙을 이용하여 자바스크립트의 조합을 사용하여 내장 HTML 검증합니다.
<input id="demo" type="number" min="5" max="10" step="1"
You can read more about forms validation in a later chapter of this tutorial.
이 튜토리얼 이후 chapter에서 양식 유효성 검사에 대한 자세한 내용을 보실 수 있습니다.
The finally Statement
finally구문을 사용하면 결과와 관계없이 try와catch후 코스를 실행 할 수 있습니다.
The finally statement lets you execute code, after try and catch, regardless of the result:
try {
Block of code to try
}
catch(err) {
Block of code to handle errors
}
finally {
Block of code to be executed regardless of the try / catch result
}
Example
function myFunction() {
var message, x;
message = document.getElementById("message");
message.innerHTML = "";
x = document.getElementById("demo").value;
try {
if(x == "") throw "is empty";
if(isNaN(x)) throw "is not a number";
x = Number(x);
if(x > 10) throw "is too high";
if(x < 5) throw "is too low";
}
catch(err) {
message.innerHTML = "Error: " + err + ".";
}
finally {
document.getElementById("demo").value = "";
}
}
JavaScript Debugging
자바스크립트 Debugging
You will soon get lost, writing JavaScript code without a debugger.
당신은 곧 debugger 없이 자바스크립트 코드를 써내려 가다가 길을 잃을 것 입니다.
JavaScript Debugging
자바스크립트 Debugging
It is difficult to write JavaScript code without a debugger.
Your code might contain syntax errors, or logical errors, that are difficult to diagnose.
Often, when JavaScript code contains errors, nothing will happen. There are no error messages, and you will get no indications where to search for errors.
Normally, errors will happen, every time you try to write some new JavaScript code.
이 debugger없이 자바스크립트 코스를 작성하기 어려울 것 입니다.
당신은 코드를 구별할 수 없는 문법 오류나, 논리적인 오류를 포함하고 있습니다.
종종 자바스크립트에서 오류가 있을 때, 아무일도 일어하지 않습니다. 오류메시지가 없습니다. 당신은 오류를 검색하는 방법에 는 표시를 얻을 수 없습니다.
일반적으로, 오류는 새로운 자바스크립트 코드를 사용하려할때 발생할 것 입니다.
JavaScript Debuggers
자바스크립트 Debuggers
Searching for errors in programming code is called code debugging.
Debugging is not easy. But fortunately, all modern browsers have a built-in debugger.
Built-in debuggers can be turned on and off, forcing errors to be reported to the user.
With a debugger, you can also set breakpoints (places where code execution can be stopped), and examine variables while the code is executing.
Normally, otherwise follow the steps at the bottom of this page, you activate debugging in your browser with the F12 key, and select “Console” in the debugger menu.
프로그램 코드에서 오류를 검색하는 것을 코드 debugging 이라고 합니다.
debugging은 쉽지 않습니다. 하지만 다행스럽게도 현재 모든 브라우저에 debuggers가 탑제되어 있습니다.
내장 debuggers는 사용자에게 보고하는 오류를 강제로 켜거나 끌 수 있습니다.
코드가 실행되는 동안 debuggers와 함께, 당신은 중단지점(코드 실행이 중지 될 수 있는 지점)을 설정하고 검사할 수 있습니다.
일반적으로, 당신의 debuggers는 당신의 브라우저의 F12키와 “Console”안에 debuggers거 메뉴가 있을 것 입니다.
The console.log() Method
console.log() 메소드
If your browser supports debugging, you can use console.log() to display JavaScript values in the debugger window:
만약 당신의 브라우저가 debugging,을 지원한다면 당신은 console.log()으로 자바스크립트 값을 윈도우 debugger 안에서 볼 수 있을 것 입니다.
Example <!DOCTYPE html>My First Web Page
Setting Breakpoints
정지지점 설정
In the debugger window, you can set breakpoints in the JavaScript code.
At each breakpoint, JavaScript will stop executing, and let you examine JavaScript values.
After examining values, you can resume the execution of code (typically with a play button).
윈도우의 debugger 안에서, 당신은 자바스크립트 코드안에 정지지점을 설정할 수 있습니다.
각가의 정지지점은, 자바스크립트가 중지되고 당신은 자바스크립트 값을 검사해야 합니다.
값을 검사한 후에는 (일반적으로는 재생버튼) 코드를 다시 시작할 수 있습니다.
The debugger Keyword
debugger 키워드
The debugger keyword stops the execution of JavaScript, and calls (if available) the debugging function.
This has the same function as setting a breakpoint in the debugger.
If no debugging is available, the debugger statement has no effect.
With the debugger turned on, this code will stop executing before it executes the third line.
debugger 키워드는 자바스크립트 실행을 중지 시키고 debugger 함수를 반환합니다.
이는 debugger에 중단점을 설정하는 것과 같은 기능을 가집니다.
어떤 debugging을 사용할 수없는 경우에는 debugger거 문은 효과가 없습니다.
debugger가 켜져 있는 코드는 세번째 줄을 실행하기 전에 중지 됩니다.
Example
var x = 15 * 5;
debugger;
document.getElementbyId("demo").innerHTML = x;
Major Browsers’ Debugging Tools
주된 브라우저 Debugging 도구들
Normally, you activate debugging in your browser with F12, and select “Console” in the debugger menu.
Otherwise follow these steps:
일반적으로, 당신은 브라우저에서 F12나 콜손의 디버그 메뉴에서 디버깅을 활성화 시킬 것 입니다.
그렇지 않다면 다음과 같이 진행합니다.
Chrome
- Open the browser.
- From the menu, select tools.
- From tools, choose developer tools.
-
Finally, select Console.
- 브라우저를 엽니다.
- 메뉴에서 도구를 선택합니다.
- 도구에서 개발자 도구를 선택합니다.
- 마지막으로, 콘솔을 선택합니다.
Firefox Firebug
- Open the browser.
- Go to the web page: http://www.getfirebug.com
-
Follow the instructions how to: install Firebug
- 브라우저를 엽니다.
- 웹페이지로 이동합니다.
- 파이어버그 설치 방법에 대한 지침을 따릅니다.
Internet Explorer
- Open the browser.
- From the menu, select tools.
- From tools, choose developer tools.
-
Finally, select Console.
- 브라우저를 엽니다.
- 메뉴에서 도구를 선택합니다.
- 도구에서 개발자 도구를 선택합니다.
- 마지막으로 콘솔을 선택합니다.
Opera
- Open the browser.
- Go to the webpage: http://dev.opera.com
-
Follow the instructions how to: add a Developer Console button to your toolbar.
- 브라우저를 엽니다.
- 웹페이지로 이동합니다.
- 어떻게 하는지 지시를 따릅니다. 도구 모음에 개발자 콘솔 버튼을 추가합니다.
Safari Firebug
- Open the browser.
- Go to the webpage: http://extensions.apple.com
-
Follow the instructions how to: install Firebug Lite.
- 브라우저를 엽니다.
- 웹페이지로 이동합니다.
- 어떻게 하는지 지시를 따릅니다. Firebug Lite설치
Safari Develop Menu
- Go to Safari, Preferences, Advanced in the main menu.
- Check “Enable Show Develop menu in menu bar”.
-
When the new option “Develop” appears in the menu: Choose “Show Error Console”.
- 주 메뉴에서 사라피 환경 설정 고급으로 이동합니다.
- 확인 메뉴표시 줄에서 메뉴를 개발 표시 사용
- 새로운 옵션 개발이 메뉴에 표시 할때 “Show Error Console” 를 선택합니다.
Did You Know?
당신은 알고 계십니까?
Debugging is the process of testing, finding, and reducing bugs (errors) in computer programs.
The first known computer bug was a real bug (an insect), stuck in the electronics.
디버깅은 발견하고 컴퓨터 프로그램의 버그를 감소 시키는 테스트하는 과정입니다. 첫번째로 알려진 컴퓨터에 실제 벌래가 갇혀 있었습니다.
ASP.NET
- OS X(10.11)에 ASP.NET Application
- OS X(10.10)에 ASP.NET 5 설치하기
- MVC Web Application에서 재사용 가능한 Authentication라이브러리 만들기
- 맥에서 ASP.NET vNext 애플리케이션 개발하기
- ASP.NET 5소개
- ASP.NET 5와 MVC 6에서 바뀌게 되는 기능 Top 10
- ASP.NET 5 스케폴딩(Scaffolding)
- MVC Controller와 ApiController의 차이점
- ASP.NET Accounts Management
- MVC를 이용해 RealGrid에 데이터를 표현하기
EF
Visual Studio
- Visual Studio Code v0.3.0
- 무서운 EF
- 해결 방법을 찾을 수 없습니다.
- GitHub Extension for Visual Studio
- Visual Studio Code for Mac
- 패러렐즈 Visual Studio Text Editor 스크롤을 부드럽게 하는 방법
Another Code
- BitBucket!! 너는 또 뭐야?
- Git! 너 뭐야?
- 슬랙앱 만들기
- 품질의 기본
- 대화의 수준
- javascript tutorial
- html tutorial
- OS X에서 Paralles Windows 10 VM의 localhost 사이트에 접속하는 방법
- OS X(10.11)에서 MongoDB
- OS X(10.11)에서 SVN(Subversion)
- OS X(10.11)에서 아파치웹서버 구동하기 (Virtual Hosting 구현)
- OS X(10.11)에서 메이븐(Maven)사용하기
- Jasmine을 이용한 Javascript 테스트
- Identicon
- 회사의 슬픔
- 지킬에서 사이드 메뉴 필터링 하기
- ASP.NET MVC vs WEB API
- 티스토리에서 구문 하이라이팅 기능 구현하기
Javascript
- react를 위한 webpack정리 (II) - 작성중
- react를 위한 webpack정리 (I)
- javascript에서 객체 정의
- Javascripting
- aws-ec2-amazon linux-nodejs
- Protractor
- AngulaJS 연습
티스토리(1) tistory(1) syntax highlighting(1) Visual Studio(3) ASP.NET(4) EF(3) RealGrid(2) Jekyll(2) GitHub(3) SqlServer(1) SqlServer 2014(1) MVC(2) ASP.NET 5(7) Identity(2) Account(1) Controller(1) ApiController(1) 스케폴딩(2) Schaffolding(2) MVC 6(1) 페러렐즈(2) Parallels(1) Liquid(1) Authentication(1) Entity Framework(2) Visual Studio Code(2) VS(2) VisualStudio(2) Visual Studio 2015(2) VS 2015(2) Extension(1) 잡설(3) Update-Database(1) Entension(1) 일을하지말아야지(1) osx(2) DNX(2) Iendticon(1) Jasmine(1) AngularJS(2) protractor(1) maven(1) java(1) OSX(5) yosemite(2) 메이븐(1) 요세미티(1) 서브라임(1) 아파치(2) apache(1) webserver(1) 웹서버(1) virtualhost(1) svn(1) subversion(1) 몽고디비(1) mongodb(2) localhost(1) 호스팅(1) hosting(1) VSCode(1) html(1) JavaScript(1) nodejs(2) aws(2) ec2(2) git(4) javascript(5) object(1) webpack(2) reactjs(2) react(2) browserify(2) 웹팩(3) 리액트(3) slack(1) api(1) slack app(1) 슬랙 앱(1) 깃(2) 깃허브(1) github(1) 비트버킷(1) BitBucket(1)
 ONLYDEL
ONLYDEL